



| Documentation: | Canadian Census 2011 |
you are here:
choose a survey
survey
document
chapter
Publisher: Statistics Canada
Survey: Canadian Census 2011
| Document: | Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary |
| citation: | Social Explorer; Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary |
Chapter Contents
Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary
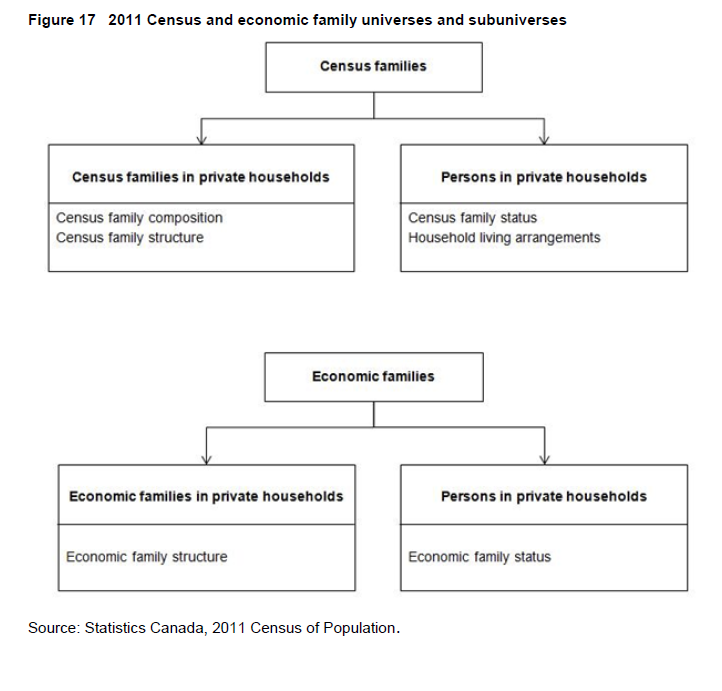
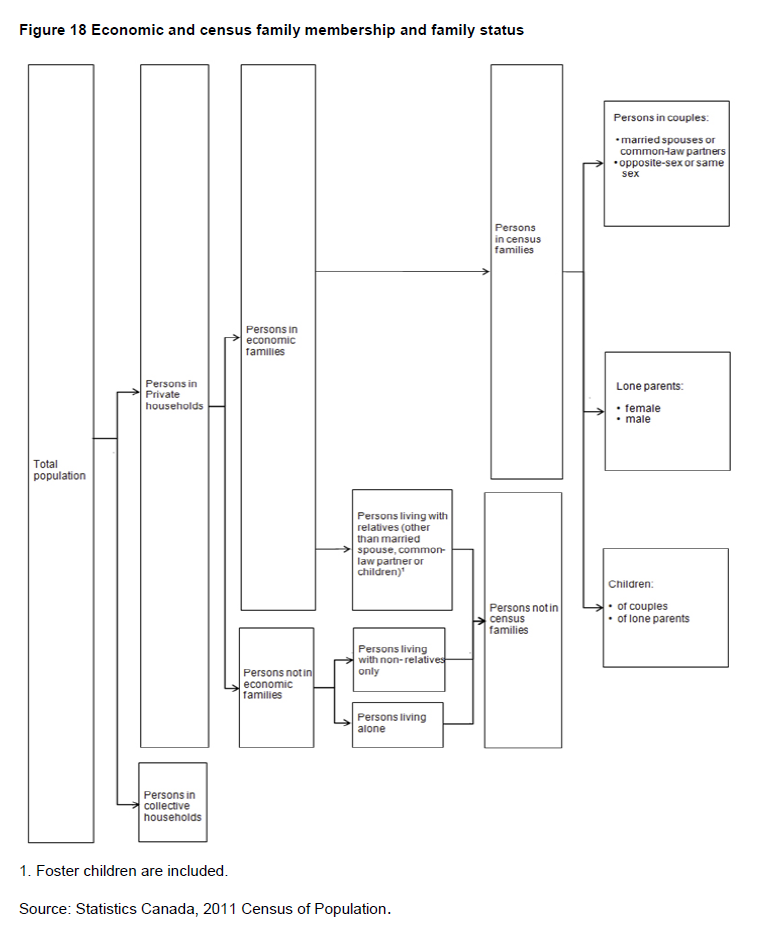
Within the family universe, two definitions of families exist: census family and economic family (see Figures 17 and 18). The related variables provide characteristics of families and of individuals in private households.


Refers to a married couple (with or without children), a common-law couple (with or without children) or a lone parent family.
Refers to a married couple (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), a common-law couple (with or without children of either and/or both partners) or a lone parent of any marital status, with at least one child. A couple may be of opposite sex or same sex. A couple family with children may be further classified as either an intact family in which all children are the biological and/or adopted children of both married spouses or of both common-law partners or a stepfamily with at least one biological or adopted child of only one married spouse or common-law partner and whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship.
Stepfamilies, in turn may be classified as simple or complex. A simple stepfamily is a couple family in which all children are biological or adopted children of one, and only one, married spouse or common-law partner whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. A complex stepfamily is a couple family which contains at least one biological or adopted child whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. These families contain children from:
Stepfamilies, in turn may be classified as simple or complex. A simple stepfamily is a couple family in which all children are biological or adopted children of one, and only one, married spouse or common-law partner whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. A complex stepfamily is a couple family which contains at least one biological or adopted child whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. These families contain children from:
- each married spouse or common-law partner and no other children
- one married spouse or common-law partner and at least one other biological or adopted child of the couple
- each married spouse or common-law partner and at least one other biological or adopted child of the couple.
'Children' refer to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, the sons or daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s). Sons or daughters who study or have a summer job elsewhere but return to live with their parent(s) during the year are considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
As of 2011, a child living with a couple family can be identified as a child in an intact family; the child of one parent in a simple stepfamily; the child of one parent in a complex stepfamily; or the child of both parents in a complex stepfamily.
As of 2006, a married couple may be of opposite or same sex.
The 2001 Census introduced several changes to the census family concept:
In the 1996, 2001 and 2006 censuses, the write-in responses for Question 6 (Relationship to Person 1) on the short questionnaire were not coded to the appropriate detailed relationship value, but were classified as 'other' relationships. Only write-in responses from the long questionnaire (20% sample) were fully coded. As a result, family characteristics are available only for the 20% sample for those years.
In censuses prior to 1991, the families of married couples and those of opposite-sex common-law couples together constituted husband-wife families and appeared as such in most census family tables.
The census family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 19 provides an overview of the census family variables.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, the sons or daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s). Sons or daughters who study or have a summer job elsewhere but return to live with their parent(s) during the year are considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
As of 2011, a child living with a couple family can be identified as a child in an intact family; the child of one parent in a simple stepfamily; the child of one parent in a complex stepfamily; or the child of both parents in a complex stepfamily.
As of 2006, a married couple may be of opposite or same sex.
The 2001 Census introduced several changes to the census family concept:
- Two persons living in a same-sex common-law relationship and their children residing in the same household, if any, are considered a census family.
- Children in a census family can have been previously married (as long as they are not currently living with a married spouse or common-law partner). Prior to the 2001 Census, they had to be never-married.
- A grandchild living in a three-generation household where the parent (middle generation) is never-married will, contrary to previous censuses, now be considered as a child in the census family of his or her parent, provided the grandchild is not living with his or her own married spouse, common-law partner, or child. Prior to the 2001 Census, the census family consisted of the two older generations.
- A grandchild present in the household of his or her grandparent(s), where a middle-generation parent is not present, will now be considered as a child in the census family of his or her grandparent, provided the grandchild is not living with his or her own married spouse, common-law partner, or child. Prior to the 2001 Census, such a grandchild would not be considered as the member of a census family.
In the 1996, 2001 and 2006 censuses, the write-in responses for Question 6 (Relationship to Person 1) on the short questionnaire were not coded to the appropriate detailed relationship value, but were classified as 'other' relationships. Only write-in responses from the long questionnaire (20% sample) were fully coded. As a result, family characteristics are available only for the 20% sample for those years.
In censuses prior to 1991, the families of married couples and those of opposite-sex common-law couples together constituted husband-wife families and appeared as such in most census family tables.
The census family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 19 provides an overview of the census family variables.
Refers to the classification of census families according to the number and/or age groups of children at home.
Refers to the classification of census families (that is, married or common-law couples, with or without children, and lone parents with at least one child) by the number and/or age group of children living at home. A couple may be of opposite or same sex. A couple with children may be further classified as either an intact family or stepfamily, and stepfamilies may, in turn, be classified as simple or complex. Children in a census family include grandchildren living with their grandparent(s) but with no parents present.
In 1971, the concept of 'children' included sons or daughters aged 24 years and younger, and never married. In 1976, the age restriction was removed, and the concept of 'children' was defined as sons or daughters of any age.
Since 2001, the concept of 'children' includes sons or daughters of any age, whether or not they have been married, provided they do not have a married spouse, common-law partner or children living in the household. Grandchildren living in the household with grandparent(s) and no parent(s) present are also considered children in the census family of their grandparent(s).
See Census family for more information on intact families and stepfamilies.
Since 2001, the concept of 'children' includes sons or daughters of any age, whether or not they have been married, provided they do not have a married spouse, common-law partner or children living in the household. Grandchildren living in the household with grandparent(s) and no parent(s) present are also considered children in the census family of their grandparent(s).
See Census family for more information on intact families and stepfamilies.
Classification of persons according to whether or not they are members of a census family and the status they have in the census family (a census family is composed of a married couple or two persons living common-law, with or without children, or of a lone parent living with at least one child in the same dwelling). A person can be a married spouse, a common-law partner, a lone parent, a child or a person not in a census family.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of a census family. (See Figure 18.)
Census family persons refer to household members who belong to a census family.
Census family persons can be further classified into one of the following four categories:
Married spouses - Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are legally married to each other and living in the same dwelling.
Common-law partners - Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are not legally married to each other, but live together as a couple in the same dwelling.
Lone parents - Mothers or fathers, with no married spouse or common-law partner present, living in a dwelling with one or more children.
Children - Blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, those sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Persons not in census families refer to household members who do not belong to a census family.
Census family persons refer to household members who belong to a census family.
Census family persons can be further classified into one of the following four categories:
Married spouses - Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are legally married to each other and living in the same dwelling.
Common-law partners - Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are not legally married to each other, but live together as a couple in the same dwelling.
Lone parents - Mothers or fathers, with no married spouse or common-law partner present, living in a dwelling with one or more children.
Children - Blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, those sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Persons not in census families refer to household members who do not belong to a census family.
Census family status is used when detail is required for persons who are part of a census family.
Common-law partners may be of any marital status other than 'Legally married (and not separated).'
The category of 'children' can be further distinguished as follows:
Common-law partners may be of any marital status other than 'Legally married (and not separated).'
The category of 'children' can be further distinguished as follows:
- Never-married sons and/or daughters in a census family.
- Ever-married sons and/or daughters in a census family, that is, who were previously married, were not included in census families according to the pre-2001 concept.
- Grandchildren living in the same household as their grandparent(s), with no parents present; these grandchildren were not included in census families according to the pre-2001 concept.
- As of 2011, a child in a couple family can be classified as either a child in an intact family or a child in a stepfamily. A child in a stepfamily, in turn, can be classified as a child in a simple stepfamily or a child in a complex stepfamily (refer to Census family for definition of intact families, stepfamilies, and simple and complex stepfamilies).
1Between 1976 and 2001, unrelated wards, foster and guardianship children are classified as lodgers rather than as sons/daughters of Person 1 (as had been the previous census practice). As of the 2006 Census, persons reported as foster children are classified as other relatives of Person 1, and are therefore in the same economic family as Person 1, but not the same census family.
2The published data for census family status for 1971, 1976, 1981 and 1986 are comparable, although census family status as defined in the Dictionary of the 1971 Census Terms (Catalogue no. 12-540) corresponds to the definition of Census family structure used from the 1976 to 2006 censuses.
In 1971, published family statistics included families living in private households (including those enumerated outside Canada) and all collective households.
2The published data for census family status for 1971, 1976, 1981 and 1986 are comparable, although census family status as defined in the Dictionary of the 1971 Census Terms (Catalogue no. 12-540) corresponds to the definition of Census family structure used from the 1976 to 2006 censuses.
In 1971, published family statistics included families living in private households (including those enumerated outside Canada) and all collective households.
Refers to the classification of census families into married couples (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), common-law couples (with or without children of either and/or both partners), and lone-parent families by sex of parent.
Refers to the classification of census families into married couples (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), common-law couples (with or without children of either and/or both partners), and lone-parent families by sex of parent. A couple may be of opposite or same sex. A couple with children may be further classified as either an intact family or stepfamily, and stepfamilies may, in turn, be classified as simple or complex. Children in a census family include grandchildren living with their grandparent(s) but with no parents present.
As of 2001, the term 'couple families' will be used when referring inclusively to families of married couples and families of common-law couples. In censuses prior to 1991, the term 'husband-wife families' used in census products covered both the families of married couples and those of opposite-sex common-law couples. Data on opposite-sex common-law couples have been available only since 1981.
As of 2001, data on same-sex common-law couples are available.
As of 2006, data on same-sex married couples are available.
As of 2011, data on intact families and stepfamilies are available.
See Census family for more information on stepfamilies.
As of 2001, data on same-sex common-law couples are available.
As of 2006, data on same-sex married couples are available.
As of 2011, data on intact families and stepfamilies are available.
See Census family for more information on stepfamilies.
Refers to a group of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling and are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship.
Refers to a group of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling and are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship. A couple may be of opposite or same sex.
The economic family concept requires only that family members be related by blood, marriage3, common-law3, adoption or a foster relationship4. By contrast, the census family concept requires that family members be a male or female married spouse, a male or female common-law partner, a male or female lone parent, or a child with a parent present. The concept of economic family may refer to a larger group of persons than does the census family concept. For example, a widowed mother living with her married son and daughter-in-law would be considered as a person not in a census family. That same person would, however, be counted as a member of an economic family along with her son and daughter-in-law. Two or more related census families living together also constitute one economic family as, for example, a husband and his wife living with their married son and daughter-in-law. Two or more adult brothers or sisters living together, apart from their parents, form an economic family, but not a census family. All census family persons are economic family persons.
The economic family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to the responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status, and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire. Figure 19 provides an overview of the economic family variables.
The economic family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to the responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status, and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire. Figure 19 provides an overview of the economic family variables.
1In 1971, published family statistics included families living in private households (including those enumerated outside Canada) and all collective households.
2As of 2001, economic families do not include Hutterite collective households. Prior to 2001, economic families were defined in Hutterite collective households.
3As of 2001, common-law partners may be of opposite or same sex. As of 2006, married spouses may be of opposite or same sex.
4As of 2006, foster children are considered economic family members.
2As of 2001, economic families do not include Hutterite collective households. Prior to 2001, economic families were defined in Hutterite collective households.
3As of 2001, common-law partners may be of opposite or same sex. As of 2006, married spouses may be of opposite or same sex.
4As of 2006, foster children are considered economic family members.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of an economic family.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of an economic family. (See Figure 17.)
Economic family persons refer to two or more household members who are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship, and thereby constitute an economic family.
Economic family persons can be further classified into one of the following two categories:
a) Economic family reference person
In each economic family, one person is designated as the reference person. In couple families, either opposite-sex or same-sex, the first person in the couple listed on the questionnaire is the economic family reference person. In lone-parent families, the male or female lone parent is the reference person. In all other economic families, the reference person is either a man or a woman not in a census family.
b) Economic family members
Persons in the economic family other than the economic family reference person are classified as the married spouse or the common-law partner of the reference person, children of the reference person (including grandchildren), or other economic family members (including foster children). Children of the reference person may be of any age or marital status.
Persons not in economic families refer to household members who do not belong to an economic family, including persons living alone.
Economic family persons refer to two or more household members who are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship, and thereby constitute an economic family.
Economic family persons can be further classified into one of the following two categories:
a) Economic family reference person
In each economic family, one person is designated as the reference person. In couple families, either opposite-sex or same-sex, the first person in the couple listed on the questionnaire is the economic family reference person. In lone-parent families, the male or female lone parent is the reference person. In all other economic families, the reference person is either a man or a woman not in a census family.
b) Economic family members
Persons in the economic family other than the economic family reference person are classified as the married spouse or the common-law partner of the reference person, children of the reference person (including grandchildren), or other economic family members (including foster children). Children of the reference person may be of any age or marital status.
Persons not in economic families refer to household members who do not belong to an economic family, including persons living alone.
Prior to 2011, the male married spouse or common-law partner was designated as the economic family reference person in opposite-sex couples, in order to produce historically comparable low-income statistics.
In 2006, grandchildren of the reference person, in the absence of the mother or father in the household, were considered as children of the reference person. In 2011, all grandchildren of the reference person are considered as children. Foster children are considered as other economic family members as of 2006.
In 1971, published family statistics included families living in private households (including those enumerated outside Canada) and all collective households.
In 2006, grandchildren of the reference person, in the absence of the mother or father in the household, were considered as children of the reference person. In 2011, all grandchildren of the reference person are considered as children. Foster children are considered as other economic family members as of 2006.
In 1971, published family statistics included families living in private households (including those enumerated outside Canada) and all collective households.
Refers to the classification of economic families as couple families, lone-parent families or other economic families.
Refers to the classification of economic families as couple families, lone-parent families or other economic families.
Couple families - Those in which a member of either a married or common-law couple is the economic family reference person.
Lone-parent families - Those in which either a male or female lone parent is the economic family reference person.
Other economic families - Those in which the economic family reference person has other relatives but does not have a married spouse or common-law partner or a child in their census family.
Couple families - Those in which a member of either a married or common-law couple is the economic family reference person.
Lone-parent families - Those in which either a male or female lone parent is the economic family reference person.
Other economic families - Those in which the economic family reference person has other relatives but does not have a married spouse or common-law partner or a child in their census family.
See Economic family status for more information on economic family reference persons.
See also 'Remarks' for Economic family.
See also 'Remarks' for Economic family.
Refers to the classification of persons as members of a family household or of a non-family household, and whether they are family persons or persons not in a census family.
Refers to the classification of persons as members of a family household or of a non-family household, that is, whether or not they are living in a household that contains at least one census family, and whether they are members of a census family or not in a census family. Persons not in census families are further classified as living with relatives, living with non-relatives (only) or living alone.
This variable provides data on household living arrangements at the population level.
This variable should be used when the distinction between persons living in family households or non-family households is important, and/or when further detail is required for persons who are not part of a census family. For more information, see Household type in the Household universe section and Census family status.
This variable should be used when the distinction between persons living in family households or non-family households is important, and/or when further detail is required for persons who are not part of a census family. For more information, see Household type in the Household universe section and Census family status.





