



| Documentation: | Canadian Census 2011 |
you are here:
choose a survey
survey
document
chapter
Publisher: Statistics Canada
Survey: Canadian Census 2011
| Document: | Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary |
| citation: | Social Explorer; Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary |
Chapter Contents
Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 98-301-X: 2011 Census Dictionary
The population universe includes variables that provide information about individuals, covering demographic characteristics and language. See Figure 16 for a list of these variables.
The population universe (target population) of the 2011 Census includes the following groups:
The population universe (target population) of the 2011 Census includes the following groups:
- Canadian citizens (by birth or by naturalization) and landed immigrants (permanent residents) with a usual place of residence in Canada.
- Canadian citizens (by birth or by naturalization) and landed immigrants (permanent residents) who are abroad either on a military base or attached to a diplomatic mission.
- Canadian citizens (by birth or by naturalization) and landed immigrants (permanent residents) at sea or in port aboard merchant vessels under Canadian registry or Canadian government vessels.
- Persons with a usual place of residence in Canada who are claiming refugee status and family members living with them.
- Persons with a usual place of residence in Canada who hold study permits and family members living with them.
- Persons with a usual place of residence in Canada who hold work permits and family members living with them.
- Government representatives of another country attached to the embassy, high commission or other diplomatic body of that country in Canada, and members of their families living with them.
- Members of the Armed Forces of another country who are stationed in Canada, and family members living with them.
- Residents of another country visiting Canada temporarily (for example, a foreign visitor on vacation or on business, with or without a visitor's permit).

Refers to a farm, ranch or other agricultural operation that produces at least one of the following products intended for sale: crops, livestock, poultry, animal products, greenhouse or nursery products, Christmas trees, mushrooms, sod, honey or bees, and maple syrup products.
A farm, ranch or other agricultural operation producing agricultural products for sale. Also includes: feedlots, greenhouses, mushroom houses and nurseries; farms producing Christmas trees, fur, game, sod, maple syrup or fruit and berries; beekeeping and poultry hatchery operations; operations with alternative livestock (bison, deer, elk, llamas, alpacas, wild boars, etc.) or alternative poultry (ostriches, emus, etc.), when the animal or derived products are intended for sale; backyard gardens if agricultural products are intended for sale; operations involved in boarding horses, riding stables and stables for housing and/or training horses even if no agriculture products are sold. Sales in the previous 12 months are not required, but there must be the intention to sell.
For the Yukon, Nunavut and Northwest Territories only, the definition also includes operations involved in the following:
- herding wild animals (such as caribou and muskox)
- breeding sled dogs
- horse outfitting and rigging
- harvesting indigenous plants and berries.
1 For the 1981 and 1986 censuses, a census farm was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding with sales of agricultural products of $250 or more during the previous 12 months. Agricultural holdings with anticipated sales of $250 or more were also included.
2For the 1976 Census, a census farm was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $1,200 or more during the year 1975. The basic unit for which a questionnaire was collected was termed 'agricultural holding'. This term was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $50 or more during the 12-month period prior to the Census Day.
3 Prior to the 1976 Census, a census farm was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $50 or more during the 12-month period prior to the Census Day.
2For the 1976 Census, a census farm was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $1,200 or more during the year 1975. The basic unit for which a questionnaire was collected was termed 'agricultural holding'. This term was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $50 or more during the 12-month period prior to the Census Day.
3 Prior to the 1976 Census, a census farm was defined as a farm, ranch or other agricultural holding of one acre or more with sales of agricultural products of $50 or more during the 12-month period prior to the Census Day.
Refers to those persons responsible for the management decisions made in the operation of the census farm.
Those persons responsible for the management decisions in operating an agricultural operation. Can be owners, tenants or hired managers of the agricultural operation, including those responsible for management decisions pertinent to particular aspects of the farm †planting, harvesting, raising animals, marketing and sales, and making capital purchases and other financial decisions. Not included are accountants, lawyers, veterinarians, crop advisors, herbicide consultants, etc. who make recommendations affecting the agricultural operation but are not ultimately responsible for management decisions.
1 Prior to the 1991 Census, the farm operator referred to only one person who was responsible for the day-to-day decisions made in the operation of an agricultural holding. Because only one operator was listed for each census farm, the number of operators was the same as the number of census farms. Beginning in 1991, up to three operators per operation could be listed on the questionnaire.
Refers to all persons living in rural areas who are members of the households of farm operators living on their census farms for any length of time during the 12-month period prior to the census.
1 Prior to 1991, only one farm operator was reported per census farm. Since 1991, up to three farm operators could be reported per census farm. Because of this change, the rural farm population count now includes all persons living in rural areas on a census farm and in the households of the first, second and third operators; before 1991, the rural farm population count included all persons living in rural areas on a census farm and in the household of the first operator. It should be noted that most of the second and third operators (usually a spouse or a child) of census farms reside in the same household as the first operator and would most likely have been included in the rural farm population under the previous method of reporting.
2 Prior to the 1981 Census, the rural farm population was defined as all persons living in rural areas in dwellings situated on census farms.
2 Prior to the 1981 Census, the rural farm population was defined as all persons living in rural areas in dwellings situated on census farms.
Refers to the age at last birthday before the reference date, that is, before May 10, 2011.
Common-law refers to two people living together as a couple but not legally married to each other.
Common-law refers to two people living together as a couple but not legally married to each other. They may be of opposite sex or of the same sex.
In the 1981 and 1986 censuses, people living common law could report their relationship by using one of the response categories in the question on relationship to Person 1; they were nonetheless included in the category 'Married' for purposes of data on marital status. For more information, see Marital status.
Since 2001, the response category 'Yes' includes same-sex common-law partners.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be not living common law.
Since 2001, the response category 'Yes' includes same-sex common-law partners.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be not living common law.
In 1966 and 1961, respondents were asked to state their age in completed years as of their last birthday before the census date. In 1961, published data for single years of age were graduated (or smoothed) within each five-year age group to counteract the tendency towards 'heaping' at certain specific ages. In 1966, this was not done, and the published tables represent the date as reported.
In 1991, 1986 and 1981, the day and month of birth were not retained for dissemination.
In 1991, 1986 and 1981, the day and month of birth were not retained for dissemination.
Refers to the marital status of the person under the law, excluding common-law status.
Refers to the marital status of the person under the law, excluding common-law status. Married spouses may be of opposite sex or of the same sex. The classification is as follows:
Single (never legally married)
A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried.
Married (and not separated)
A person who is married and has neither separated nor divorced, and whose spouse is living.
Separated
A person who is married but who is no longer living with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce.
Divorced
A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried.
Widowed
A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried.
Single (never legally married)
A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried.
Married (and not separated)
A person who is married and has neither separated nor divorced, and whose spouse is living.
Separated
A person who is married but who is no longer living with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce.
Divorced
A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried.
Widowed
A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried.
Never legally married; Legally married (and not separated); Separated, but still legally married; Divorced; Widowed
Since 1991, the addition of a question solely on common-law status has made it possible to separate the concept of common-law status from that of legal marital status and to provide accurate data on both these concepts.
In 2011, the category 'Never legally married' on the questionnaire was changed (previously 'Never legally married (single)'), but the concept did not change. Since 2006, the category 'Married' includes legally married same-sex spouses.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married).
In 2011, the category 'Never legally married' on the questionnaire was changed (previously 'Never legally married (single)'), but the concept did not change. Since 2006, the category 'Married' includes legally married same-sex spouses.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married).
Refers to the marital status of the person, taking into account his/her common-law status.
Refers to the marital status of the person, taking into account his/her common-law status. Persons who are married or living common law may be of opposite sex or of the same sex.
The classification is as follows:
Married (and not separated)
A person who is married and has not separated or obtained a divorce, and whose spouse is living.
Common-law
A person who is living with another person as a couple but who is not legally married to that person.
Separated
A person who is married but who no longer lives with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Divorced
A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Widowed
A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Single (never legally married)
A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
The classification is as follows:
Married (and not separated)
A person who is married and has not separated or obtained a divorce, and whose spouse is living.
Common-law
A person who is living with another person as a couple but who is not legally married to that person.
Separated
A person who is married but who no longer lives with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Divorced
A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Widowed
A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Single (never legally married)
A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Before 1981, data on marital status were collected using a single question. In the 1981 and 1986 censuses, people living common law could report their common-law status by using one of the response categories in the question on relationship to Person 1; they were nonetheless included in the category 'Married' for purposes of data on marital status. Since 1991, the addition of a question solely on common law has made it possible to separate the concept of common-law status from that of legal marital status and to provide accurate data on both these concepts. The data from both questions can be combined to derive the classification, 'Marital status.'
In 2011, the category 'Never legally married' on the questionnaire was changed (previously 'Never legally married (single)'), but the concept did not change. Since 2006, the category 'Married' includes legally married same-sex spouses. Since 2001, the category 'Common-law' includes same-sex common-law partners. In 1961 and 1966, separated persons were included with married persons.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married) and not living common law.
In 2011, the category 'Never legally married' on the questionnaire was changed (previously 'Never legally married (single)'), but the concept did not change. Since 2006, the category 'Married' includes legally married same-sex spouses. Since 2001, the category 'Common-law' includes same-sex common-law partners. In 1961 and 1966, separated persons were included with married persons.
All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married) and not living common law.
Person who lives in an institutional collective dwelling, such as a hospital, a nursing home or a jail. This includes residents under care or custody and employee residents and family members living with them, if any.
Institutional collective dwellings are general and speciality hospitals, chronic care and long-term care hospitals, nursing homes, group homes or institutions for the physically handicapped and treatment centres, group homes for children and youth, group homes or institutions for people with psychiatric disorders or developmental disabilities, federal correctional institutions, provincial and territorial custodial facilities, young offenders' facilities, jails and police lock-up facilities, shelters for persons lacking a fixed address, shelters for abused women and their children and other shelters and lodging with assistance services.
In the 2001 and 2006 censuses, tabulations for the non-institutional population excluded all residents of institutional collective dwellings, both resident under care or custody and resident employees and family members living with them. In the 1996, 1991, 1986 and 1981 censuses, resident employees and their families were included in data for the non-institutional population.
In 1981, the term 'Inmates' was used.
In the 2001 and 2006 censuses, tabulations for the non-institutional population excluded all residents of institutional collective dwellings, both resident under care or custody and resident employees and family members living with them. In the 1996, 1991, 1986 and 1981 censuses, resident employees and their families were included in data for the non-institutional population.
In 1981, the term 'Inmates' was used.
Refers to the number of children in private households by age groups. To be included, children must live in the same household as the family, without a married spouse, common-law partner or one or more of their children living in the same household. In a census family, they may be children by birth, marriage or adoption. In an economic family, foster children are also included.
'Children' refers to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as to grandchildren in households where there are no parents present.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own sons and/or daughters, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
As of the 2001 Census, several changes were made to the census family concepts. For additional information, see the Census family composition and Census family status definitions in the family universe.
Historically comparable data on presence of children and labour force activity dating back to the 1971 Census are available for females 15 years and over in private households. Similar data are available for males dating back to 1996.
Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own sons and/or daughters, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
As of the 2001 Census, several changes were made to the census family concepts. For additional information, see the Census family composition and Census family status definitions in the family universe.
Historically comparable data on presence of children and labour force activity dating back to the 1971 Census are available for females 15 years and over in private households. Similar data are available for males dating back to 1996.
Refers to the question about the relationship of household members to the first person reported on the questionnaire for the household, called Person 1.
Refers to the question about the relationship of household members to the first person reported on the questionnaire for the household, called Person 1. A household member may be related to Person 1 through blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship or unrelated (e.g., lodger, room-mate or employee). This question is used to obtain information on families, as well as the family characteristics of individuals.
Person 1; Opposite-sex husband or wife; Opposite-sex common-law partner; Same-sex married spouse; Same-sex common-law partner; Son or daughter of Person 1 only; Son or daughter of both Persons 1 and 2; Son or daughter of Person 2 only; Son-in-law or daughter-in-law; Grandchild; Father or mother; Father-in-law or mother-in-law; Brother or sister; Foster child; Room-mate, lodger or boarder; Other - Specify1Remarks Three different categories for son or daughter allow information on stepchildren to be captured. Prior to 2011, there was a single response category, 'Son or daughter of Person 1'.
As of the 2011 Census, 'Foster child' is a response category.
As of the 2011 Census, there are two response categories for married spouse of Person 1 to distinguish between opposite-sex and same-sex married spouses. In the 2006 Census, information on opposite-sex and same-sex married spouses was obtained from the responses to 'Husband or wife of Person 1' in conjunction with responses to sex (Question 2). In addition, 'same-sex married spouse' was included as an example for the write-in category of 'Other - Specify'.
As of the 2001 Census, there are two response categories for common-law partner of Person 1, to distinguish between opposite-sex and same-sex common-law partners.
In the 1996, 2001 and 2006 censuses, the write-in responses for the category 'Other - Specify' on the short questionnaire were not coded to the appropriate detailed relationship value, but were classified as 'other' relationships.
Only write-in responses from the long questionnaire (20% sample) were fully coded. As a result, family characteristics are available only for the 20% sample for those years.
Regarding the order in which to list household members on the questionnaire, there is an instruction to 'begin the list with an adult followed, if applicable, by that person's spouse or common-law partner and by their children'.
Previous wording of the instruction in the census has varied, but the meaning has stayed the same. One exception is that in 1971, Person 1, then called the 'head of household', was defined as 'the husband rather than the wife' in a married couple. In 1976, this was changed to 'either the husband or the wife'.
As of the 2011 Census, 'Foster child' is a response category.
As of the 2011 Census, there are two response categories for married spouse of Person 1 to distinguish between opposite-sex and same-sex married spouses. In the 2006 Census, information on opposite-sex and same-sex married spouses was obtained from the responses to 'Husband or wife of Person 1' in conjunction with responses to sex (Question 2). In addition, 'same-sex married spouse' was included as an example for the write-in category of 'Other - Specify'.
As of the 2001 Census, there are two response categories for common-law partner of Person 1, to distinguish between opposite-sex and same-sex common-law partners.
In the 1996, 2001 and 2006 censuses, the write-in responses for the category 'Other - Specify' on the short questionnaire were not coded to the appropriate detailed relationship value, but were classified as 'other' relationships.
Only write-in responses from the long questionnaire (20% sample) were fully coded. As a result, family characteristics are available only for the 20% sample for those years.
Regarding the order in which to list household members on the questionnaire, there is an instruction to 'begin the list with an adult followed, if applicable, by that person's spouse or common-law partner and by their children'.
Previous wording of the instruction in the census has varied, but the meaning has stayed the same. One exception is that in 1971, Person 1, then called the 'head of household', was defined as 'the husband rather than the wife' in a married couple. In 1976, this was changed to 'either the husband or the wife'.
In general, the usual place of residence is the dwelling in Canada in which a person lives most of the time.
In most cases, people have only one residence. This dwelling is therefore their usual place of residence (main residence).
However, there are a number of situations where the process is not elementary and special rules have been created in order to define an individual's usual place of residence.
However, there are a number of situations where the process is not elementary and special rules have been created in order to define an individual's usual place of residence.
- Persons with more than one residence
This category includes all persons who have more than one dwelling in Canada that could be considered by them as their usual place of residence. In this situation, the usual place of residence is the place where a person spends the major part of the year. If the time spent at each residence is equal or the person is not sure which one to choose, the residence where he or she stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011 should be considered as his or her usual place of residence.
However, there are two exceptions to this general rule:
(a) Sons or daughters who live somewhere else while attending school, but return to live with their parents part of the year, should consider the residence they share with their parents as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
(b) Husbands, wives or common-law partners who live away from their families while working, but return to their families regularly (for example, on weekends), should consider the residence they share with their spouse or partner as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
- Persons in institutions (such as a hospital, a nursing home, a prison or a correctional centre)
Persons with no other usual place of residence elsewhere in Canada, or persons who have been in one or more institutions for a continuous period of six months or longer, are to be considered usual residents of the institution.
- Residents with no usual place of residence
Residents who do not have a usual place of residence should be enumerated in the dwelling where they stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011.
- Persons residing outside Canada
Canadian citizens and landed immigrants residing outside Canada on the reference day (particularly persons aboard Canadian government or merchant vessels, Canadian government employees (federal and provincial) and their family, and members of the Canadian Armed Forces and their family) who do not have a permanent place of residence within Canada occupied by one or more family members, were asked to provide on the Census questionnaire the address they use for election purposes or their last permanent address within Canada. This information is then used to determine a geographic location for defining their usual place of residence.
The concept of usual place of residence is necessary to ensure that residents of Canada are counted once and only once. The use of this concept means that the Canadian census is a de jure census, as opposed to a de facto census. Thus, individuals are counted at their usual place of residence, regardless of where they are found on Census Day. The de jure method has been used since 1871.
Refers to a variable specified within the framework of the Official Languages Act.
2011 (100% population), 2006 (1/5 sample), 2001 (1/5 sample), 1996 (1/5 sample), 1991 (1/5 sample), 1986 (1/5 sample)
This variable was derived within the framework of the application of the Official Languages Act.
This derivation method is described in the regulations concerning the use of official languages for the provision of public services. It takes into account, first the knowledge of the two official languages, second the mother tongue, and third, the home language.
People who can conduct a conversation in French only are assigned French as their first official language spoken. People who can carry on a conversation in English only are assigned English as their first official language spoken.
The responses to questions on mother tongue and language spoken most often at home are subsequently used to establish the first official language spoken by people who speak both English and French, or who cannot speak either of the two official languages. The French category includes people who have French only or French and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue. People who have English only or English and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue are included in the English category. For cases that have not yet been classified, people are assigned to the French category when they speak French only or French and at least one non-official language as their language spoken most often at home. The procedure is the same for English. Thus, the population is classified into two principal categories: English or French. It is necessary to add two residual categories for people who cannot be classified in accordance with the information available: English and French and neither English nor French.
Please consult the following documents for more information: Official Languages (Communications with and Services to the Public) Regulations, registered on December 16, 1991, in accordance with section 85 of the Official Languages Act, R.S.C., c. 32 (4th Suppl.) and Population Estimates by First Official Language Spoken, 1991, Catalogue no. 94-320, Demography Division, Statistics Canada.
This derivation method is described in the regulations concerning the use of official languages for the provision of public services. It takes into account, first the knowledge of the two official languages, second the mother tongue, and third, the home language.
People who can conduct a conversation in French only are assigned French as their first official language spoken. People who can carry on a conversation in English only are assigned English as their first official language spoken.
The responses to questions on mother tongue and language spoken most often at home are subsequently used to establish the first official language spoken by people who speak both English and French, or who cannot speak either of the two official languages. The French category includes people who have French only or French and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue. People who have English only or English and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue are included in the English category. For cases that have not yet been classified, people are assigned to the French category when they speak French only or French and at least one non-official language as their language spoken most often at home. The procedure is the same for English. Thus, the population is classified into two principal categories: English or French. It is necessary to add two residual categories for people who cannot be classified in accordance with the information available: English and French and neither English nor French.
Please consult the following documents for more information: Official Languages (Communications with and Services to the Public) Regulations, registered on December 16, 1991, in accordance with section 85 of the Official Languages Act, R.S.C., c. 32 (4th Suppl.) and Population Estimates by First Official Language Spoken, 1991, Catalogue no. 94-320, Demography Division, Statistics Canada.
Refers to the language spoken most often or on a regular basis at home by the individual on May 10, 2011.
2011 (100% population), 2006 (1/5 sample), 2001 (1/5 sample), 1996 (1/5 sample), 1991 (1/5 sample), 1986 (1/5 sample), 1981 (1/5 sample), 1971 (1/3 sample)
This question was changed after the 1996 Census. Until that census, the question asked individuals for the language spoken most often at home, which now represents part (a) of the question that has been asked since 2001. Part (b) on other languages spoken on a regular basis at home has been added since 2001. This was done in order to reflect a more complete picture of the linguistic situation of Canadian households.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly asked on the long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006, and 2011.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly asked on the long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006, and 2011.
Some 2011 Census data on home language by type of response (for example, 'spoken regularly') cannot be compared with census data in 1996 and before, since the second part of the question on home language, asked for the first time in 2001, relates to the other language(s) spoken on a regular basis at home. The category 'Single responses' means that the language reported is the only one spoken most often at home while the category 'Multiple responses' indicates that at least two languages have been reported as spoken most often at home.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
Refers to the language spoken most often at home by the individual on May 10, 2011. Data on other languages spoken on a regular basis at home are also collected.
2011 (100% population), 2006 (1/5 sample), 2001 (1/5 sample), 1996 (1/5 sample), 1991 (1/5 sample), 1986 (1/5 sample), 1981 (1/5 sample), 1971 (1/3 sample)
This question was changed after the 1996 Census. Until that census, the question asked individuals for the language spoken most often at home, which now represents part (a) of the question that has been asked since 2001. Part (b) on other languages spoken on a regular basis at home has been added since 2001. This was done in order to reflect a more complete picture of the linguistic situation of Canadian households.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly on long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006 and 2011.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly on long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006 and 2011.
Some 2011 Census data on home language by type of response (for example, 'spoken regularly') cannot be compared with census data in 1996 and before, since the second part of the question on home language, asked for the first time in 2001, relates to the other language(s) spoken on a regular basis at home. The category 'Single responses' means that the language reported is the only one spoken most often at home while the category 'Multiple responses' indicates that at least two languages have been reported as spoken most often at home.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
Refers to the other language(s) spoken on a regular basis at home by the individual on May 10, 2011. Data on language spoken most often at home were also collected.
This question was added after the 1996 Census. Until that census, the question asked individuals for the language spoken most often at home, which now represents part (a) of the question that has been asked since 2001. This part (part [b]) on languages spoken on a regular basis at home was added since 2001. This was done in order to reflect a more complete portrait of the linguistic situation of Canadian households.
In 2011, the following instructions for question 8, part (a) and part (b), were provided to respondents in the 2011 Census Guide:
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly on long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006 and 2011.
In 2011, the following instructions for question 8, part (a) and part (b), were provided to respondents in the 2011 Census Guide:
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear has been modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French.' The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages, formerly on long form census questionnaires, also reflect this change, in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006 and 2011.
Some 2011 Census data on home language by type of response (for example, 'spoken regularly') cannot be compared with census data in 1996 and before, since the second part of the question on home language, asked for the first time in 2001, relates to the other language (s) spoken on a regular basis at home. The category 'Single responses' means that the language reported is the only one spoken most often at home while the category 'Multiple responses' indicates that at least two languages have been reported as spoken most often at home.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
When comparing 2011 Census data on home language with data from 1996 or before, only the language spoken most often at home is to be used since, before the 2001 Census, there was no question asked regarding other languages spoken on a regular basis.
The categories 'Only' and 'Mostly' were derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the single responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. The category 'Equally' was derived to obtain the frequency of language spoken at home from the multiple responses reported in part (a) of the question on home language. Finally, the category 'Regularly' was created from the responses reported in the second part of the question pertaining to home language, asked for the first time in 2001.
Refers to the ability to conduct a conversation in English only, in French only, in both English and French, or in neither English nor French.
2011 (100% population), 2006 (1/5 sample), 2001 (1/5 sample), 1996 (1/5 sample), 1991 (1/5 sample), 1986 (1/5 sample), 1981 (1/5 sample), 1971 (1/3 sample).
The official language data are based on the respondent's assessment of his or her ability to speak the two official languages.
This is the same question as in 2006, 2001, 1996 and 1991.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear was modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French'. The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages also reflect this change in the actual wording of the questions.
This is the same question as in 2006, 2001, 1996 and 1991.
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there is a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appear was modified since 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French'. The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages also reflect this change in the actual wording of the questions.
Refers to the first language learned at home in childhood and still understood by the individual on May 10, 2011.
For the first time in 2011, the mother tongue question is not the only language question asked of the entire population. In 2011, as on previous long form census questionnaires since 1991, the question on mother tongue appears after the knowledge of official language and home language questions.
In the wording of the question on mother tongue, the expression 'at home' was added to specify the context in which the individual learned the language. Only the two official languages, English and French, appeared on the questionnaire. Other languages could be written in the space provided, as in 2006, 2001, 1996 and 1991. In previous censuses, the most frequently occurring non-official languages were listed on the questionnaire.
To facilitate respondents' task an instruction which appeared in the 1986 Census Guide was added to the questionnaire in 1991, where it remained in 1996, 2001, 2006, and 2011. The instruction read as follows: 'If this person no longer understands the first language learned, indicate the second language learned.'
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there was a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appeared was modified after 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French'. The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages also reflected this change in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006, and 2011.
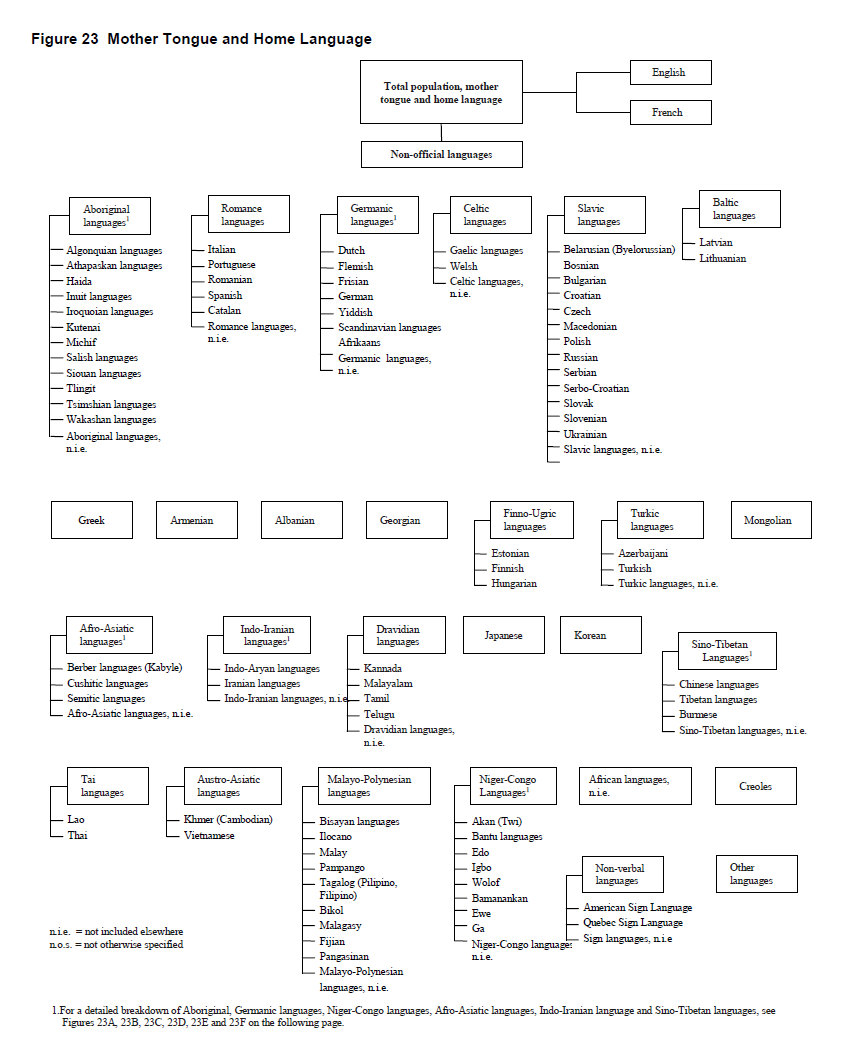
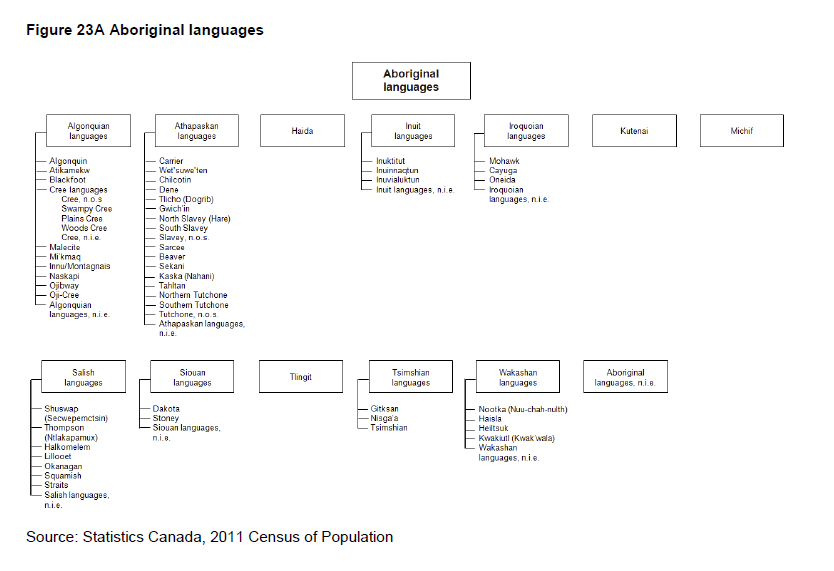
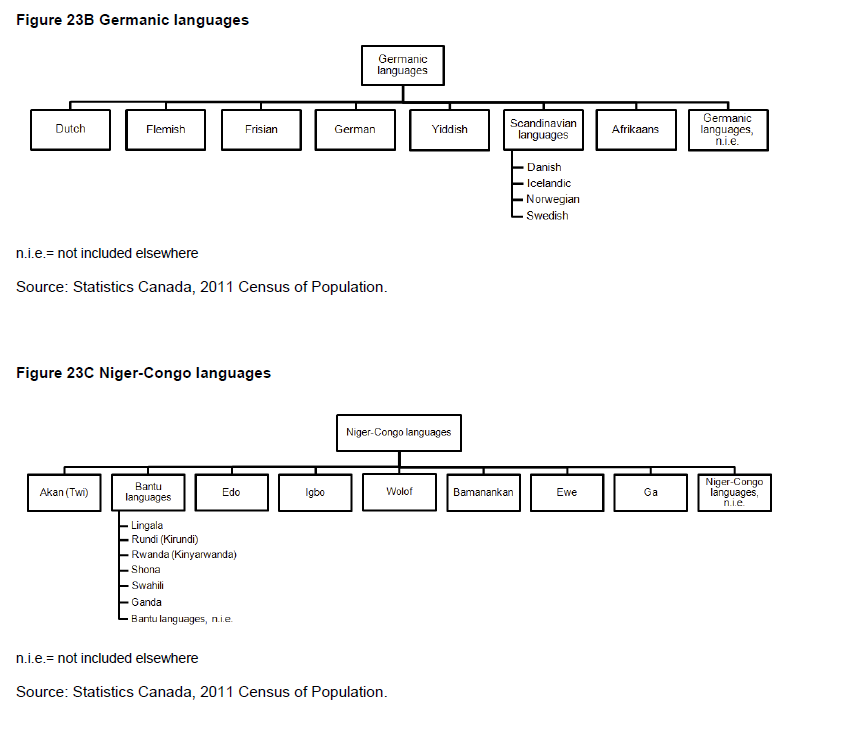
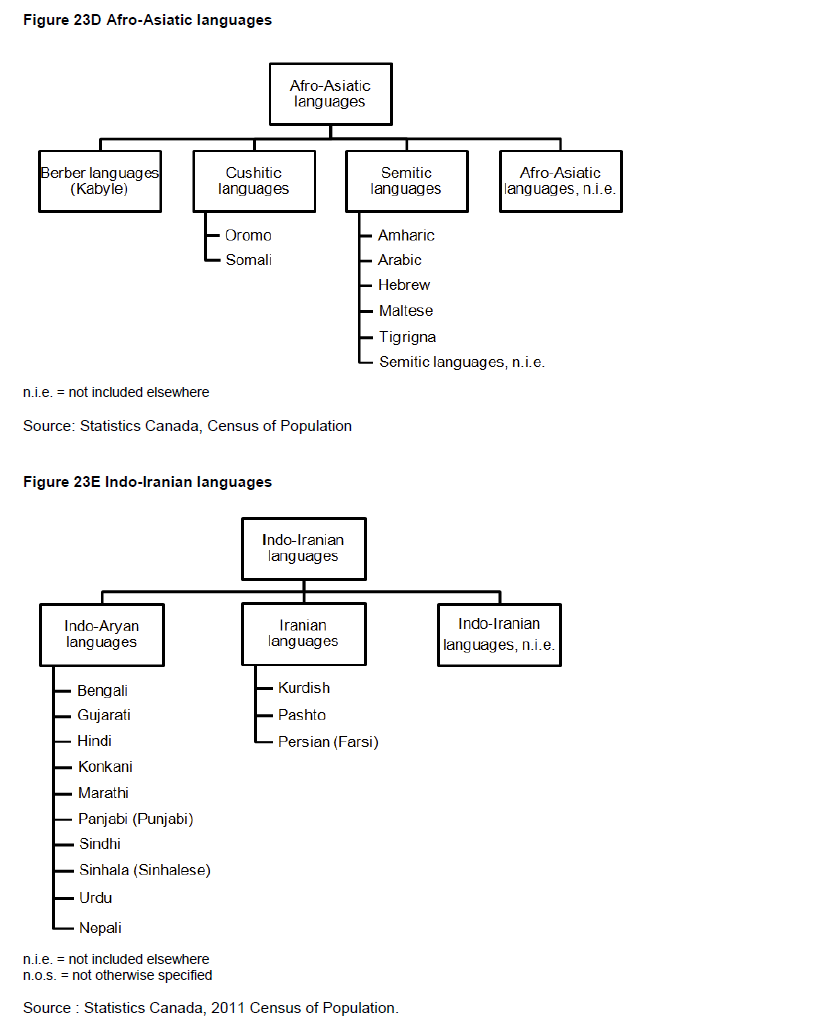

In the wording of the question on mother tongue, the expression 'at home' was added to specify the context in which the individual learned the language. Only the two official languages, English and French, appeared on the questionnaire. Other languages could be written in the space provided, as in 2006, 2001, 1996 and 1991. In previous censuses, the most frequently occurring non-official languages were listed on the questionnaire.
To facilitate respondents' task an instruction which appeared in the 1986 Census Guide was added to the questionnaire in 1991, where it remained in 1996, 2001, 2006, and 2011. The instruction read as follows: 'If this person no longer understands the first language learned, indicate the second language learned.'
On the French version of all census forms, for all questions in the language module where there was a choice of response available, the order in which the choices appeared was modified after 1996 in order to give precedence to the category 'French'. The questions on knowledge of official languages and non-official languages also reflected this change in the actual wording of the questions.
For comparability purposes, Appendix D provides a list of languages released in 2001, 2006, and 2011.









