



| Documentation: | Canadian Census 2011 |
you are here:
choose a survey
survey
document
chapter
Publisher: Statistics Canada
Survey: Canadian Census 2011
| Document: | Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 99-000-X2011001 National Household Survey |
| citation: | Social Explorer; Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 99-000-X2011001 National Household Survey |
Chapter Contents
Refers to difficulties with carrying out daily activities and whether the amount or kind of activities that can be done are reduced due to physical or mental conditions or health problems.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Questions 7 and 8
Responses: Question 7: Difficulties with daily activities:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Question 8: Reduction in activities:
(a) at home:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
(b) at work or at school:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Not applicable
(c) in other activities:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Remarks: In 2011, the following instructions were provided to NHS respondents:
1. These questions refer to conditions or health problems that have lasted or are expected to last six months or more.
2. For young children, consider only those conditions or problems that have been diagnosed by a professional.
Questions 7 and 8 provide information on the number of people in Canada who have difficulties with daily activities, and whose activities are reduced because of a physical or mental condition or a health problem. These questions, which are intended to only be used as filter questions for a follow up survey, do not provide an estimate of disability in Canada.
The 2012 Canadian Survey on Disability (CSD), which is conducted as a follow up survey to the NHS, is the main source of disability data in Canada. The population covered by the CSD includes all adults who answered 'yes' to either of the activity limitation questions on the NHS.
The main reason that responses to the NHS filter questions cannot be used to estimate disability in Canada is the large number of 'false positives.' In other words, a respondent reported a limitation on the NHS but did not report a disability on the CSD. There can be a number of reasons for these false positives. For example, the response may have been obtained by proxy whereby the person answering the NHS believed that the individual in question had some type of activity limitation or disability, however, the individual does not consider him or herself to have any type of limitation at the time of the CSD. Other examples of false positives are persons who were injured, sick or recovering from surgery at the time of the NHS but no longer limited in their activities at the time of the CSD.
As a result of this phenomenon, it is essential that users of the NHS Activity Limitation data be aware that the filter questions cannot be used on their own as an estimate of the population with a disability.
Activity limitation data from the 2011 NHS will be available upon special request only. These data have minimum edits and should be used with caution.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Questions 7 and 8
Responses: Question 7: Difficulties with daily activities:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Question 8: Reduction in activities:
(a) at home:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
(b) at work or at school:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Not applicable
(c) in other activities:
Yes, sometimes
Yes, often
No
Remarks: In 2011, the following instructions were provided to NHS respondents:
1. These questions refer to conditions or health problems that have lasted or are expected to last six months or more.
2. For young children, consider only those conditions or problems that have been diagnosed by a professional.
Questions 7 and 8 provide information on the number of people in Canada who have difficulties with daily activities, and whose activities are reduced because of a physical or mental condition or a health problem. These questions, which are intended to only be used as filter questions for a follow up survey, do not provide an estimate of disability in Canada.
The 2012 Canadian Survey on Disability (CSD), which is conducted as a follow up survey to the NHS, is the main source of disability data in Canada. The population covered by the CSD includes all adults who answered 'yes' to either of the activity limitation questions on the NHS.
The main reason that responses to the NHS filter questions cannot be used to estimate disability in Canada is the large number of 'false positives.' In other words, a respondent reported a limitation on the NHS but did not report a disability on the CSD. There can be a number of reasons for these false positives. For example, the response may have been obtained by proxy whereby the person answering the NHS believed that the individual in question had some type of activity limitation or disability, however, the individual does not consider him or herself to have any type of limitation at the time of the CSD. Other examples of false positives are persons who were injured, sick or recovering from surgery at the time of the NHS but no longer limited in their activities at the time of the CSD.
As a result of this phenomenon, it is essential that users of the NHS Activity Limitation data be aware that the filter questions cannot be used on their own as an estimate of the population with a disability.
Activity limitation data from the 2011 NHS will be available upon special request only. These data have minimum edits and should be used with caution.
Refers to the age at last birthday before the reference date, that is, before May 10, 2011.
Refers to a married couple (with or without children), a common-law couple (with or without children) or a lone parent family.
Refers to a married couple (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), a common-law couple (with or without children of either and/or both partners) or a lone parent of any marital status, with at least one child. A couple may be of opposite sex or same sex. A couple family with children may be further classified as either an intact family in which all children are the biological and/or adopted children of both married spouses or of both common-law partners or a stepfamily with at least one biological or adopted child of only one married spouse or common-law partner and whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. Stepfamilies, in turn may be classified as simple or complex. A simple stepfamily is a couple family in which all children are biological or adopted children of one, and only one, married spouse or common-law partner whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. A complex stepfamily is a couple family which contains at least one biological or adopted child whose birth or adoption preceded the current relationship. These families contain children from:
- each married spouse or common-law partner and no other children
- one married spouse or common-law partner and at least one other biological or adopted child of the couple
- each married spouse or common-law partner and at least one other biological or adopted child of the couple.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: 'Children' refer to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, the sons or daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s). Sons or daughters who study or have a summer job elsewhere but return to live with their parent(s) during the year are considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
The census family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 1.4 provides an overview of the census family variables.
Figure 1.4 Overview of the Census Family and Economic Family Variables
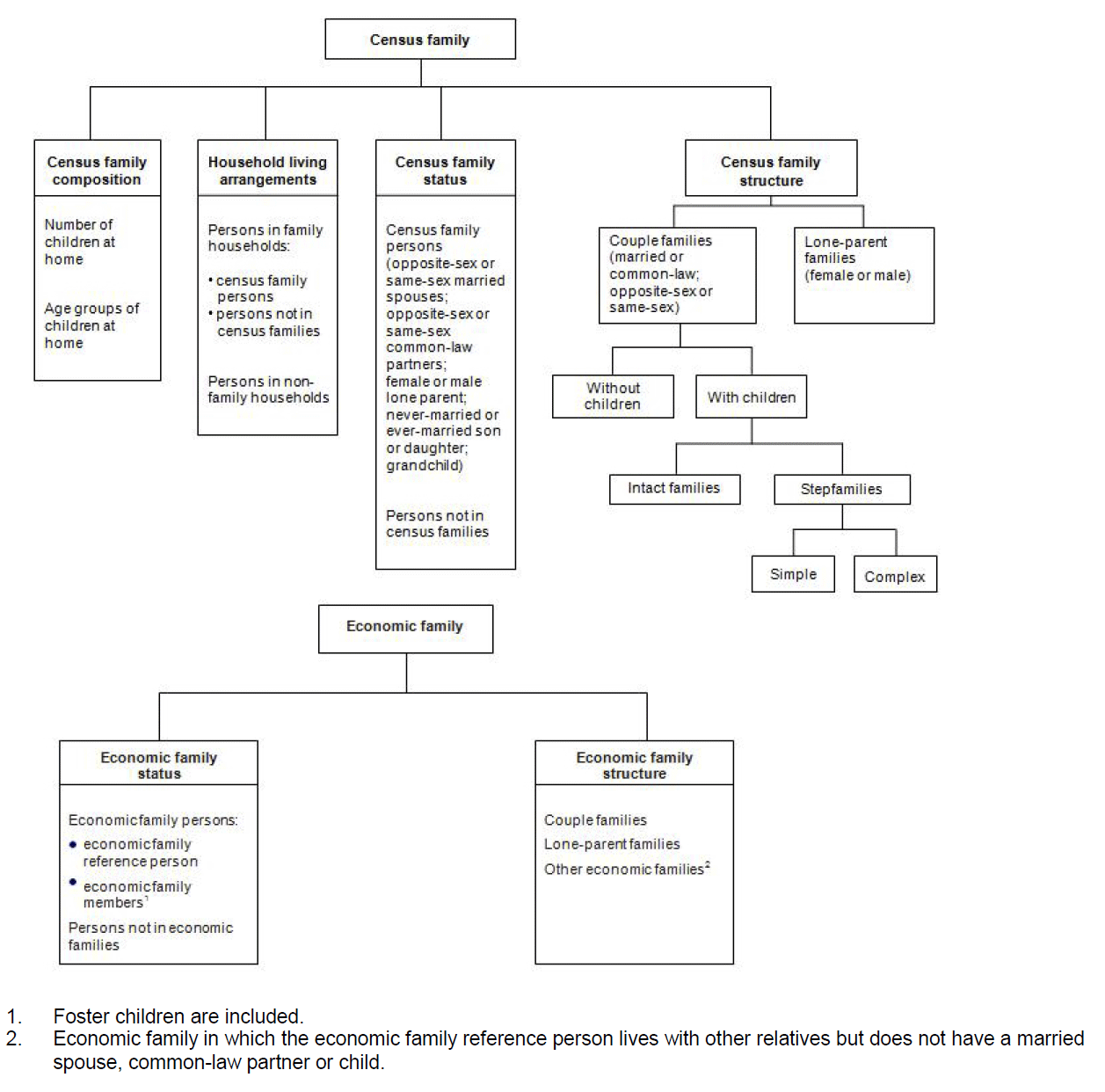
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: 'Children' refer to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, the sons or daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s). Sons or daughters who study or have a summer job elsewhere but return to live with their parent(s) during the year are considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
The census family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common-law status and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 1.4 provides an overview of the census family variables.
Figure 1.4 Overview of the Census Family and Economic Family Variables

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the classification of census families according to the number and/or age groups of children at home.
Refers to the classification of census families (that is, married or common-law couples, with or without children, and lone parents with at least one child) by the number and/or age group of children living at home. A couple may be of opposite or same sex. A couple with children may be further classified as either an intact family or stepfamily, and stepfamilies may, in turn, be classified as simple or complex. Children in a census family include grandchildren living with their grandparent(s) but with no parents present.
Classification of persons according to whether or not they are members of a census family and the status they have in the census family (a census family is composed of a married couple or two persons living common-law, with or without children, or of a lone parent living with at least one child in the same dwelling). A person can be a married spouse, a common-law partner, a lone parent, a child or a person not in a census family.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of a census family. (See Figure 1.3.)
Census family persons refer to household members who belong to a census family.
Census family persons can be further classified into one of the following four categories:
(a) Married spouses
Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are legally married to each other and living in the same dwelling.
(b) Common-law partners
Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are not legally married to each other, but live together as a couple in the same dwelling.
(c) Lone parents
Mothers or fathers, with no married spouse or common-law partner present, living in a dwelling with one or more children.
(d) Children
Blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, those sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Persons not in census families refer to household members who do not belong to a census family.
Census family persons refer to household members who belong to a census family.
Census family persons can be further classified into one of the following four categories:
(a) Married spouses
Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are legally married to each other and living in the same dwelling.
(b) Common-law partners
Two persons of opposite sex or of the same sex who are not legally married to each other, but live together as a couple in the same dwelling.
(c) Lone parents
Mothers or fathers, with no married spouse or common-law partner present, living in a dwelling with one or more children.
(d) Children
Blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age or marital status) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own children, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, those sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Persons not in census families refer to household members who do not belong to a census family.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: Census family status is used when detail is required for persons who are part of a census family.
Common-law partners may be of any marital status other than 'Legally married (and not separated).'
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: Census family status is used when detail is required for persons who are part of a census family.
Common-law partners may be of any marital status other than 'Legally married (and not separated).'
Refers to the classification of census families into married couples (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), common-law couples (with or without children of either and/or both partners), and lone-parent families by sex of parent.
Refers to the classification of census families into married couples (with or without children of either and/or both spouses), common-law couples (with or without children of either and/or both partners), and lone-parent families by sex of parent. A couple may be of opposite or same sex. A couple with children may be further classified as either an intact family or stepfamily, and stepfamilies may, in turn, be classified as simple or complex. Children in a census family include grandchildren living with their grandparent(s) but with no parents present.
Refers to a farm, ranch or other agricultural operation that produces at least one of the following products intended for sale: crops, livestock, poultry, animal products, greenhouse or nursery products, Christmas trees, mushrooms, sod, honey or bees, and maple syrup products.
A farm, ranch or other agricultural operation producing agricultural products for sale. Also includes: feedlots, greenhouses, mushroom houses and nurseries; farms producing Christmas trees, fur, game, sod, maple syrup or fruit and berries; beekeeping and poultry hatchery operations; operations with alternative livestock (bison, deer, elk, llamas, alpacas, wild boars, etc.) or alternative poultry (ostriches, emus, etc.), when the animal or derived products are intended for sale; backyard gardens if agricultural products are intended for sale; operations involved in boarding horses, riding stables and stables for housing and/or training horses even if no agriculture products are sold. Sales in the previous 12 months are not required, but there must be the intention to sell.
Note: For the Yukon, Nunavut and Northwest Territories only, the definition also includes operations involved in the following:
Note: For the Yukon, Nunavut and Northwest Territories only, the definition also includes operations involved in the following:
- herding wild animals (such as caribou and muskox)
- breeding sled dogs
- horse outfitting and rigging
- harvesting indigenous plants and berries.
Common-law refers to two people living together as a couple but not legally married to each other.
Common-law refers to two people living together as a couple but not legally married to each other. They may be of opposite sex or of the same sex.
A separate set of living quarters in which a person or a group of persons live permanently.
Refers to a separate set of living quarters with a private entrance either from outside or from a common hall, lobby, vestibule or stairway inside the building in which a person or a group of persons is permanently residing. The entrance to the dwelling must be one that can be used without passing through the living quarters of someone else. Also included are private dwellings whose usual residents are temporarily absent on May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Figure 1.9 for an illustration of the private dwelling occupied by usual residents universe.
The number of private dwellings occupied by usual residents is equal to the number of private households.
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Figure 1.9 for an illustration of the private dwelling occupied by usual residents universe.
The number of private dwellings occupied by usual residents is equal to the number of private households.
Refers to a group of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling and are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship.
Refers to a group of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling and are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship. A couple may be of opposite or same sex.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: The economic family concept requires only that family members be related by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship. By contrast, the census family concept requires that family members be a male or female married spouse, a male or female common-law partner, a male or female lone parent, or a child with a parent present. The concept of economic family may refer to a larger group of persons than does the census family concept. For example, a widowed mother living with her married son and daughter-in-law would be considered as a person not in a census family. That same person would, however, be counted as a member of an economic family along with her son and daughter-in-law. Two or more related census families living together also constitute one economic family as, for example, a husband and his wife living with their married son and daughter-in-law. Two or more adult brothers or sisters living together, apart from their parents, form an economic family, but not a census family. All census family persons are economic family persons.
The economic family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to the responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common law status, and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 1.4 provides an overview of the economic family variables.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: The economic family concept requires only that family members be related by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship. By contrast, the census family concept requires that family members be a male or female married spouse, a male or female common-law partner, a male or female lone parent, or a child with a parent present. The concept of economic family may refer to a larger group of persons than does the census family concept. For example, a widowed mother living with her married son and daughter-in-law would be considered as a person not in a census family. That same person would, however, be counted as a member of an economic family along with her son and daughter-in-law. Two or more related census families living together also constitute one economic family as, for example, a husband and his wife living with their married son and daughter-in-law. Two or more adult brothers or sisters living together, apart from their parents, form an economic family, but not a census family. All census family persons are economic family persons.
The economic family and its associated classifications and variables are derived according to the responses to the questions on sex, date of birth, marital status, common law status, and relationship to Person 1. In addition, consideration is given to the order in which household members are listed on the questionnaire.
Figure 1.4 provides an overview of the economic family variables.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of an economic family.
Refers to the classification of the population according to whether or not the persons are members of an economic family. (See Figure 1.4.)
Economic family persons refer to two or more household members who are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship, and thereby constitute an economic family.
Economic family persons can be further classified into one of the following two categories:
(a) Economic family reference person
In each economic family, one person is designated as the reference person. In couple families, either opposite-sex or same-sex, the first person in the couple listed on the questionnaire is the economic family reference person. In lone-parent families, the male or female lone parent is the reference person. In all other economic families, the reference person is either a man or a woman not in a census family.
(b) Economic family members
Persons in the economic family other than the economic family reference person are classified as the married spouse or the common-law partner of the reference person, children of the reference person (including grandchildren), or other economic family members (including foster children). Children of the reference person may be of any age or marital status.
Persons not in economic families refer to household members who do not belong to an economic family, including persons living alone.
Economic family persons refer to two or more household members who are related to each other by blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship, and thereby constitute an economic family.
Economic family persons can be further classified into one of the following two categories:
(a) Economic family reference person
In each economic family, one person is designated as the reference person. In couple families, either opposite-sex or same-sex, the first person in the couple listed on the questionnaire is the economic family reference person. In lone-parent families, the male or female lone parent is the reference person. In all other economic families, the reference person is either a man or a woman not in a census family.
(b) Economic family members
Persons in the economic family other than the economic family reference person are classified as the married spouse or the common-law partner of the reference person, children of the reference person (including grandchildren), or other economic family members (including foster children). Children of the reference person may be of any age or marital status.
Persons not in economic families refer to household members who do not belong to an economic family, including persons living alone.
Refers to the classification of economic families as couple families, lone-parent families or other economic families.
Refers to the classification of economic families as couple families, lone-parent families or other economic families.
Couple families – Those in which a member of either a married or common-law couple is the economic family reference person.
Lone-parent families – Those in which either a male or female lone parent is the economic family reference person.
Other economic families – Those in which the economic family reference person has other relatives but does not have a married spouse or common-law partner or a child in their census family.
Couple families – Those in which a member of either a married or common-law couple is the economic family reference person.
Lone-parent families – Those in which either a male or female lone parent is the economic family reference person.
Other economic families – Those in which the economic family reference person has other relatives but does not have a married spouse or common-law partner or a child in their census family.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Economic families in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Economic family status for more information on economic family reference persons.
See also 'Remarks' for Economic family.br />
Reported for: Economic families in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Economic family status for more information on economic family reference persons.
See also 'Remarks' for Economic family.br />
Refers to those persons responsible for the management decisions made in the operation of the census farm.
Those persons responsible for the management decisions in operating an agricultural operation. Can be owners, tenants or hired managers of the agricultural operation, including those responsible for management decisions pertinent to particular aspects of the farm — planting, harvesting, raising animals, marketing and sales, and making capital purchases and other financial decisions. Not included are accountants, lawyers, veterinarians, crop advisors, herbicide consultants, etc. who make recommendations affecting the agricultural operation but are not ultimately responsible for management decisions.
Refers to the classification of persons as members of a family household or of a non-family household, and whether they are family persons or persons not in a census family.
Refers to the classification of persons as members of a family household or of a non-family household, that is, whether or not they are living in a household that contains at least one census family, and whether they are members of a census family or not in a census family. Persons not in census families are further classified as living with relatives, living with non-relatives (only) or living alone.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: This variable provides data on household living arrangements at the population level.
This variable should be used when the distinction between persons living in family households or non-family households is important, and/or when further detail is required for persons who are not part of a census family. For more information, see Household type in the Household universe section and Census family status.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Derived variable: Questions 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: This variable provides data on household living arrangements at the population level.
This variable should be used when the distinction between persons living in family households or non-family households is important, and/or when further detail is required for persons who are not part of a census family. For more information, see Household type in the Household universe section and Census family status.
Refers to the basic division of private households into family and non-family households. Family household refers to a household that contains at least one census family, that is, a married couple with or without children, or a couple living common law with or without children, or a lone parent living with one or more children (lone-parent family). One-family household refers to a single census family (with or without other persons) that occupies a private dwelling. Multiple-family household refers to a household in which two or more census families (with or without additional persons) occupy the same private dwelling. Family households may also be divided based on the presence of persons not in a census family.
Non-family household refers to either one person living alone in a private dwelling or to a group of two or more people who share a private dwelling, but who do not constitute a census family.
Non-family household refers to either one person living alone in a private dwelling or to a group of two or more people who share a private dwelling, but who do not constitute a census family.
Refers to a person or a group of persons (other than foreign residents) who occupy the same private dwelling and do not have a usual place of residence elsewhere in Canada. Household members who are temporarily absent on May 10, 2011 (e.g., temporarily residing elsewhere) are considered as part of their usual household. Every person is a member of one and only one household.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Figure 1.8 for an illustration of the private households universe and subuniverses.
The number of private households is equal to the number of private dwellings occupied by usual residents.
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: See Figure 1.8 for an illustration of the private households universe and subuniverses.
The number of private households is equal to the number of private dwellings occupied by usual residents.
Refers to the marital status of the person under the law, excluding common-law status.
Refers to the marital status of the person under the law, excluding common-law status. Married spouses may be of opposite sex or of the same sex. The classification is as follows:
Single (never legally married): A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried.
Married (and not separated): A person who is married and has neither separated nor divorced, and whose spouse is living.
Separated: A person who is married but who is no longer living with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce.
Divorced: A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried.
Widowed: A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried.
Single (never legally married): A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried.
Married (and not separated): A person who is married and has neither separated nor divorced, and whose spouse is living.
Separated: A person who is married but who is no longer living with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce.
Divorced: A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried.
Widowed: A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 4
Responses: Never legally married; Legally married (and not separated); Separated, but still legally married; Divorced; Widowed
Remarks: All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married).
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 4
Responses: Never legally married; Legally married (and not separated); Separated, but still legally married; Divorced; Widowed
Remarks: All persons under 15 years of age are considered to be single (never legally married).
Refers to the marital status of the person, taking into account his/her common-law status..
Refers to the marital status of the person, taking into account his/her common-law status. Persons who are married or living common law may be of opposite sex or of the same sex.The classification is as follows:
Married (and not separated): A person who is married and has not separated or obtained a divorce, and whose spouse is living.
Common-law: A person who is living with another person as a couple but who is not legally married to that person.
Separated: A person who is married but who no longer lives with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Divorced: A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Widowed: A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Single (never legally married): A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Married (and not separated): A person who is married and has not separated or obtained a divorce, and whose spouse is living.
Common-law: A person who is living with another person as a couple but who is not legally married to that person.
Separated: A person who is married but who no longer lives with his/her spouse (for any reason other than illness, work or school) and who has not obtained a divorce. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Divorced: A person who has obtained a legal divorce and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Widowed: A person who has lost his/her spouse through death and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Single (never legally married): A person who has never married or a person whose marriage has been annulled and who has not remarried. Persons living common law are not included in this category.
Refers to the number of children in private households by age groups. To be included, children must live in the same household as the family, without a married spouse, common-law partner or one or more of their children living in the same household. In a census family, they may be children by birth, marriage or adoption. In an economic family, foster children are also included.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population aged 15 years and over in private households
Question no.: Derived variable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: 'Children' refers to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as to grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own sons and/or daughters, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Reported for: Population aged 15 years and over in private households
Question no.: Derived variable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: 'Children' refers to blood, step or adopted sons and daughters (regardless of age) who are living in the same dwelling as their parent(s), as well as to grandchildren in households where there are no parents present. Sons and daughters who are living with their married spouse or common-law partner, or with one or more of their own sons and/or daughters, are not considered to be members of the census family of their parent(s), even if they are living in the same dwelling. In addition, sons and daughters who do not live in the same dwelling as their parent(s) are not considered members of the census family of their parent(s).
Refers to the question about the relationship of household members to the first person reported on the questionnaire for the household, called Person 1.
Refers to the question about the relationship of household members to the first person reported on the questionnaire for the household, called Person 1. A household member may be related to Person 1 through blood, marriage, common-law, adoption or a foster relationship or unrelated (e.g., lodger, room-mate or employee). This question is used to obtain information on families, as well as the family characteristics of individuals.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 6
Responses: Person 1; Opposite-sex husband or wife; Opposite-sex common-law partner; Same-sex married spouse; Same-sex common‑law partner; Son or daughter of Person 1 only; Son or daughter of both Persons 1 and 2; Son or daughter of Person 2 only; Son-in-law or daughter-in-law; Grandchild; Father or mother; Father-in-law or mother-in-law; Brother or sister; Foster child; Room-mate, lodger or boarder; Other – Specify
Remarks: Not applicable
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 6
Responses: Person 1; Opposite-sex husband or wife; Opposite-sex common-law partner; Same-sex married spouse; Same-sex common‑law partner; Son or daughter of Person 1 only; Son or daughter of both Persons 1 and 2; Son or daughter of Person 2 only; Son-in-law or daughter-in-law; Grandchild; Father or mother; Father-in-law or mother-in-law; Brother or sister; Foster child; Room-mate, lodger or boarder; Other – Specify
Remarks: Not applicable
Refers to all persons living in rural areas who are members of the households of farm operators living on their census farms for any length of time during the 12-month period prior to the census.
Characteristics that define a dwelling’s structure, for example, the characteristics of a single-detached house, a semi-detached house, a row house, or an apartment or flat in a duplex.
Refers to the structural characteristics and/or dwelling configuration, that is, whether the dwelling is a single-detached house, an apartment in a high-rise building, a row house, a mobile home, etc.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Private dwellings occupied by usual residents
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Single-detached house – A single dwelling not attached to any other dwelling or structure (except its own garage or shed). A single-detached house has open space on all sides, and has no dwellings either above it or below it. A mobile home fixed permanently to a foundation is also classified as a single-detached house.
Semi-detached house – One of two dwellings attached side by side (or back to back) to each other, but not attached to any other dwelling or structure (except its own garage or shed). A semi-detached dwelling has no dwellings either above it or below it, and the two units together have open space on all sides.
Row house – One of three or more dwellings joined side by side (or occasionally side to back), such as a townhouse or garden home, but not having any other dwellings either above or below.
Townhouses attached to a high-rise building are also classified as row houses.
Apartment or flat in a duplex – One of two dwellings, located one above the other, may or may not be attached to other dwellings or buildings.
Apartment in a building that has five or more storeys – A dwelling unit in a high-rise apartment building which has five or more storeys.
Apartment in a building that has fewer than five storeys – A dwelling unit attached to other dwelling units, commercial units, or other non-residential space in a building that has fewer than five storeys.
Other single-attached house – A single dwelling that is attached to another building and that does not fall into any of the other categories, such as a single dwelling attached to a non-residential structure (e.g., a store or a church) or occasionally to another residential structure (e.g., an apartment building).
Mobile home – A single dwelling, designed and constructed to be transported on its own chassis and capable of being moved to a new location on short notice. It may be placed temporarily on a foundation pad and may be covered by a skirt.
Other movable dwelling – A single dwelling, other than a mobile home, used as a place of residence, but capable of being moved on short notice, such as a tent, recreational vehicle, travel trailer, houseboat or floating home.
Remarks: A linked home (a single house which is not attached to any other dwelling above ground) is classified as a 'single-detached house'.
Reported for: Private dwellings occupied by usual residents
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Single-detached house – A single dwelling not attached to any other dwelling or structure (except its own garage or shed). A single-detached house has open space on all sides, and has no dwellings either above it or below it. A mobile home fixed permanently to a foundation is also classified as a single-detached house.
Semi-detached house – One of two dwellings attached side by side (or back to back) to each other, but not attached to any other dwelling or structure (except its own garage or shed). A semi-detached dwelling has no dwellings either above it or below it, and the two units together have open space on all sides.
Row house – One of three or more dwellings joined side by side (or occasionally side to back), such as a townhouse or garden home, but not having any other dwellings either above or below.
Townhouses attached to a high-rise building are also classified as row houses.
Apartment or flat in a duplex – One of two dwellings, located one above the other, may or may not be attached to other dwellings or buildings.
Apartment in a building that has five or more storeys – A dwelling unit in a high-rise apartment building which has five or more storeys.
Apartment in a building that has fewer than five storeys – A dwelling unit attached to other dwelling units, commercial units, or other non-residential space in a building that has fewer than five storeys.
Other single-attached house – A single dwelling that is attached to another building and that does not fall into any of the other categories, such as a single dwelling attached to a non-residential structure (e.g., a store or a church) or occasionally to another residential structure (e.g., an apartment building).
Mobile home – A single dwelling, designed and constructed to be transported on its own chassis and capable of being moved to a new location on short notice. It may be placed temporarily on a foundation pad and may be covered by a skirt.
Other movable dwelling – A single dwelling, other than a mobile home, used as a place of residence, but capable of being moved on short notice, such as a tent, recreational vehicle, travel trailer, houseboat or floating home.
Remarks: A linked home (a single house which is not attached to any other dwelling above ground) is classified as a 'single-detached house'.
In general, the usual place of residence is the dwelling in Canada in which a person lives most of the time.
In most cases, people have only one residence. This dwelling is therefore their usual place of residence (main residence).
However, there are a number of situations where the process is not elementary and special rules have been created in order to define an individual’s usual place of residence.
1. Persons with more than one residence
This category includes all persons who have more than one dwelling in Canada that could be considered by them as their usual place of residence. In this situation, the usual place of residence is the place where a person spends the major part of the year. If the time spent at each residence is equal or the person is not sure which one to choose, the residence where he or she stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011 should be considered as his or her usual place of residence.
However, there are two exceptions to this general rule:
(a) Sons or daughters who live somewhere else while attending school, but return to live with their parents part of the year, should consider the residence they share with their parents as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
(b) Husbands, wives or common-law partners who live away from their families while working, but return to their families regularly (for example, on weekends), should consider the residence they share with their spouse or partner as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
2. Persons in an institution (such as a hospital, a nursing home, a prison or a correctional centre)
Persons in an institution who have been there for less than six months and who have another place of residence in Canada should consider the other residence as his or her usual place of residence.
3. Residents with no usual place of residence
Residents who do not have a usual place of residence should be enumerated in the dwelling where they stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011.
However, there are a number of situations where the process is not elementary and special rules have been created in order to define an individual’s usual place of residence.
1. Persons with more than one residence
This category includes all persons who have more than one dwelling in Canada that could be considered by them as their usual place of residence. In this situation, the usual place of residence is the place where a person spends the major part of the year. If the time spent at each residence is equal or the person is not sure which one to choose, the residence where he or she stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011 should be considered as his or her usual place of residence.
However, there are two exceptions to this general rule:
(a) Sons or daughters who live somewhere else while attending school, but return to live with their parents part of the year, should consider the residence they share with their parents as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
(b) Husbands, wives or common-law partners who live away from their families while working, but return to their families regularly (for example, on weekends), should consider the residence they share with their spouse or partner as their usual place of residence, even if they spend most of the year elsewhere.
2. Persons in an institution (such as a hospital, a nursing home, a prison or a correctional centre)
Persons in an institution who have been there for less than six months and who have another place of residence in Canada should consider the other residence as his or her usual place of residence.
3. Residents with no usual place of residence
Residents who do not have a usual place of residence should be enumerated in the dwelling where they stayed overnight between May 9 and 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: The concept of usual place of residence is necessary to ensure that we have counted everyone we need to count and that no one is counted twice. Thus, individuals are counted at their usual place of residence, regardless of where they are found on the reference day.
Reported for: Not applicable
Question no.: Not applicable
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: The concept of usual place of residence is necessary to ensure that we have counted everyone we need to count and that no one is counted twice. Thus, individuals are counted at their usual place of residence, regardless of where they are found on the reference day.




