



| Documentation: | Canadian Census 2011 |
you are here:
choose a survey
survey
document
chapter
Publisher: Statistics Canada
Survey: Canadian Census 2011
| Document: | Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 99-000-X2011001 National Household Survey |
| citation: | Social Explorer; Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 99-000-X2011001 National Household Survey |
Chapter Contents
Statistics Canada - Catalogue no. 99-000-X2011001 National Household Survey
Age at immigration refers to the age at which the respondent first obtained landed immigrant/permanent resident status.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 3 and 12
Responses: Range of values: single years of age from 0 to 110
Remarks: Age at immigration is calculated using the year of immigration, the year of birth, and an estimated month of immigration.
Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 are not landed immigrants, will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12). These people are either Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) or are non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who has a work or study permit or who is a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living in Canada with them.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status and Year of immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of age of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 3 and 12
Responses: Range of values: single years of age from 0 to 110
Remarks: Age at immigration is calculated using the year of immigration, the year of birth, and an estimated month of immigration.
Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 are not landed immigrants, will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12). These people are either Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) or are non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who has a work or study permit or who is a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living in Canada with them.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status and Year of immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of age of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Citizenship refers to the legal citizenship status of a person. Citizenship can be by birth or naturalization. A person may have more than one citizenship. A person may be stateless, that is, they may have no citizenship.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 10
Responses: Response categories included 'Canada, by birth,' 'Canada, by naturalization,' and 'Other country - Specify.' A write-in space for country of citizenship (other than Canada) was provided. Respondents were asked to indicate more than one citizenship, if applicable. Refer to Appendix 1.6 for the classification of countries of citizenship for the 2011 National Household Survey.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS citizenship question asked: 'Of what country is this person a citizen?' Note accompanying the citizenship question stated:
Indicate more than one citizenship, if applicable.
'Canada, by naturalization' refers to the process by which an immigrant is granted citizenship of Canada, under the Citizenship Act.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in Canada, unless-at the time of their birth-one or both parents were government representatives of another country (for example, in diplomatic service) and neither parent was a Canadian citizen or a landed immigrant:
- mark 'Canada, by birth.'
For persons born outside Canada if, at the time of their birth, one or both parents were Canadian citizens:
- mark 'Canada, by birth.'
For persons who have applied for, and have been granted, Canadian citizenship (for example, persons who have been issued a Canadian citizenship certificate):
- mark 'Canada, by naturalization.'
For persons who were born outside Canada and have not become Canadian citizens:
- report under 'Other country' the name of the other country for which they hold citizenship.
For persons who are dual citizens of Canada and another country, do not report 'dual citizenship':
- mark either 'Canada, by birth' or 'Canada, by naturalization,' and report the name of the other country.
For further information on this population, refer to Figure 1.6 - Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents: Citizenship.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of citizenship data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.6 Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents - Citizenship
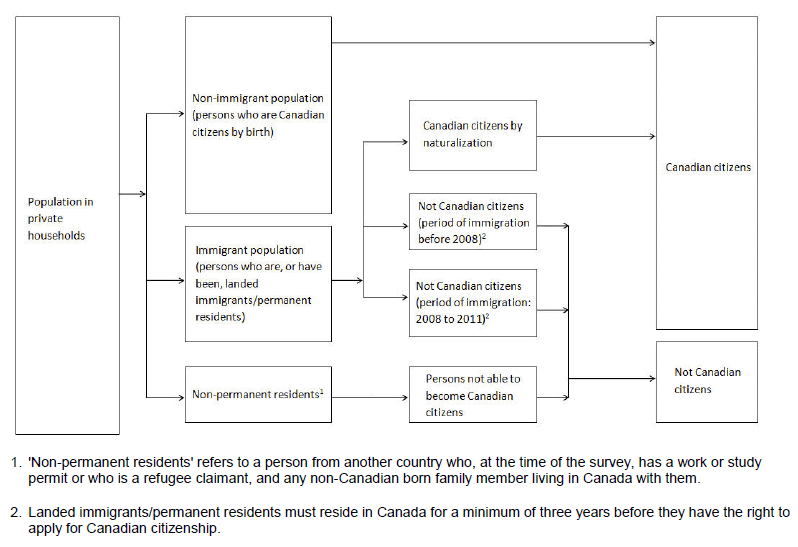
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 10
Responses: Response categories included 'Canada, by birth,' 'Canada, by naturalization,' and 'Other country - Specify.' A write-in space for country of citizenship (other than Canada) was provided. Respondents were asked to indicate more than one citizenship, if applicable. Refer to Appendix 1.6 for the classification of countries of citizenship for the 2011 National Household Survey.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS citizenship question asked: 'Of what country is this person a citizen?' Note accompanying the citizenship question stated:
Indicate more than one citizenship, if applicable.
'Canada, by naturalization' refers to the process by which an immigrant is granted citizenship of Canada, under the Citizenship Act.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in Canada, unless-at the time of their birth-one or both parents were government representatives of another country (for example, in diplomatic service) and neither parent was a Canadian citizen or a landed immigrant:
- mark 'Canada, by birth.'
For persons born outside Canada if, at the time of their birth, one or both parents were Canadian citizens:
- mark 'Canada, by birth.'
For persons who have applied for, and have been granted, Canadian citizenship (for example, persons who have been issued a Canadian citizenship certificate):
- mark 'Canada, by naturalization.'
For persons who were born outside Canada and have not become Canadian citizens:
- report under 'Other country' the name of the other country for which they hold citizenship.
For persons who are dual citizens of Canada and another country, do not report 'dual citizenship':
- mark either 'Canada, by birth' or 'Canada, by naturalization,' and report the name of the other country.
For further information on this population, refer to Figure 1.6 - Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents: Citizenship.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of citizenship data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.6 Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents - Citizenship

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Ethnic origin refers to the ethnic or cultural origins of the respondent's ancestors.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 17
Responses: Respondents were asked to specify as many origins as applicable in Question 17: Ethnic origin. Four lines were provided for write-in responses and up to six ethnic origins were retained. Refer to Appendix 1.2 for the 2011 National Household Survey classification for ethnic origin.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Ethnic origin question asked: 'What were the ethnic or cultural origins of this person's ancestors?'
A note provided above the question stated that 'This question collects information on the ancestral origins of the population and provides information about the composition of Canada's diverse population.'
Below the question, a second note indicated that 'An ancestor is usually more distant than a grandparent' and examples of ethnic origins were listed as follows: Canadian, English, French, Chinese, East Indian, Italian, German, Scottish, Irish, Cree, Mi'kmaq, Salish, Métis, Inuit, Filipino, Dutch, Ukrainian, Polish, Portuguese, Greek, Korean, Vietnamese, Jamaican, Jewish, Lebanese, Salvadorean, Somali, Colombian, etc.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
This question refers to the ethnic or cultural origin or origins of a person's ancestors. Other than Aboriginal persons, most people can trace their origins to their ancestors who first came to this continent. Ancestry should not be confused with citizenship or nationality.
For all persons, report the specific ethnic or cultural group or groups to which their ancestors belonged, not the language they spoke. For example, report 'Haitian' rather than 'French,' or 'Austrian' rather than 'German.'
For persons of East Indian or South Asian origins, report a specific origin or origins. Do not report 'Indian.' For example, report 'East Indian from India,' 'East Indian from Guyana,' or indicate the specific group, such as 'Punjabi' or 'Tamil.'
For persons with Aboriginal ancestors, report a specific origin or origins. For example, report 'Cree,' 'Mikmaq,' 'Ojibway,' 'Métis,' or 'North American Indian.' Do not report 'Indian.'
Comparability of ethnic origin data across data sources (such as the 2011 NHS and 2006 Census) is affected by differences in survey collection methodology; question wording, format, examples and instructions; changes in data processing; and the social environment at the time of data collection.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of ethnic origin data, refer to the Ethnic Origin Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 17
Responses: Respondents were asked to specify as many origins as applicable in Question 17: Ethnic origin. Four lines were provided for write-in responses and up to six ethnic origins were retained. Refer to Appendix 1.2 for the 2011 National Household Survey classification for ethnic origin.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Ethnic origin question asked: 'What were the ethnic or cultural origins of this person's ancestors?'
A note provided above the question stated that 'This question collects information on the ancestral origins of the population and provides information about the composition of Canada's diverse population.'
Below the question, a second note indicated that 'An ancestor is usually more distant than a grandparent' and examples of ethnic origins were listed as follows: Canadian, English, French, Chinese, East Indian, Italian, German, Scottish, Irish, Cree, Mi'kmaq, Salish, Métis, Inuit, Filipino, Dutch, Ukrainian, Polish, Portuguese, Greek, Korean, Vietnamese, Jamaican, Jewish, Lebanese, Salvadorean, Somali, Colombian, etc.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
This question refers to the ethnic or cultural origin or origins of a person's ancestors. Other than Aboriginal persons, most people can trace their origins to their ancestors who first came to this continent. Ancestry should not be confused with citizenship or nationality.
For all persons, report the specific ethnic or cultural group or groups to which their ancestors belonged, not the language they spoke. For example, report 'Haitian' rather than 'French,' or 'Austrian' rather than 'German.'
For persons of East Indian or South Asian origins, report a specific origin or origins. Do not report 'Indian.' For example, report 'East Indian from India,' 'East Indian from Guyana,' or indicate the specific group, such as 'Punjabi' or 'Tamil.'
For persons with Aboriginal ancestors, report a specific origin or origins. For example, report 'Cree,' 'Mikmaq,' 'Ojibway,' 'Métis,' or 'North American Indian.' Do not report 'Indian.'
Comparability of ethnic origin data across data sources (such as the 2011 NHS and 2006 Census) is affected by differences in survey collection methodology; question wording, format, examples and instructions; changes in data processing; and the social environment at the time of data collection.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of ethnic origin data, refer to the Ethnic Origin Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to a variable specified within the framework of the Official Languages Act.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 13, 15 and 16
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: This variable was derived within the framework of the application of the Official Languages Act.
This derivation method is described in the regulations concerning the use of official languages for the provision of public services. It takes into account, first, the knowledge of the two official languages, second, the mother tongue, and third, the home language.
People who can conduct a conversation in French only are assigned French as their first official language spoken. People who can carry on a conversation in English only are assigned English as their first official language spoken. The responses to questions on mother tongue and language spoken most often at home are subsequently used to establish the first official language spoken by people who speak both English and French, or who cannot speak either of the two official languages. The French category includes people who have French only or French and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue. People who have English only or English and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue are included in the English category. For cases that have not yet been classified, people are
assigned to the French category when they speak French only or French and at least one non-official language as their language spoken most often at home. The procedure is the same for English. Thus, the population is classified into two principal categories: English or French. It is necessary to add two residual categories for people who cannot be classified in accordance with the information available: English and French and neither English nor French.
Please consult the following documents for more information: Official Languages (Communications with and Services to the Public) Regulations, registered on
December 16, 1991, in accordance with section 85 of the Official Languages Act, R.S.C., c. 32 (4th Suppl.) and Population Estimates by First Official Language Spoken, 1991, Catalogue no. 94-320, Demography Division, Statistics Canada.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 13, 15 and 16
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: This variable was derived within the framework of the application of the Official Languages Act.
This derivation method is described in the regulations concerning the use of official languages for the provision of public services. It takes into account, first, the knowledge of the two official languages, second, the mother tongue, and third, the home language.
People who can conduct a conversation in French only are assigned French as their first official language spoken. People who can carry on a conversation in English only are assigned English as their first official language spoken. The responses to questions on mother tongue and language spoken most often at home are subsequently used to establish the first official language spoken by people who speak both English and French, or who cannot speak either of the two official languages. The French category includes people who have French only or French and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue. People who have English only or English and at least one non-official language as their mother tongue are included in the English category. For cases that have not yet been classified, people are
assigned to the French category when they speak French only or French and at least one non-official language as their language spoken most often at home. The procedure is the same for English. Thus, the population is classified into two principal categories: English or French. It is necessary to add two residual categories for people who cannot be classified in accordance with the information available: English and French and neither English nor French.
Please consult the following documents for more information: Official Languages (Communications with and Services to the Public) Regulations, registered on
December 16, 1991, in accordance with section 85 of the Official Languages Act, R.S.C., c. 32 (4th Suppl.) and Population Estimates by First Official Language Spoken, 1991, Catalogue no. 94-320, Demography Division, Statistics Canada.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Generation status refers to whether or not the person or the person's parents were born in Canada. It identifies persons as being first generation, second generation or third generation or more.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 9 and 25(a) and 25(b)
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: Generation status is derived from responses to questions concerning the person's place of birth (Question 9) and the place of birth of his or her parents (Question 25).
For more information on the place of birth questions in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definitions of Place of birth of respondent, Place of birth of father and Place of birth of mother.
Within the generation status variable, the three main categories are defined as follows:
'First generation' includes persons who were born outside Canada. For the most part, these are people who are now, or have ever been, immigrants to Canada.
'Second generation' includes persons who were born in Canada and had at least one parent born outside Canada. For the most part, these are the children of immigrants.
'Third generation or more' includes persons who were born in Canada with both parents born in Canada.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of generation status data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 9 and 25(a) and 25(b)
Responses: Not applicable
Remarks: Generation status is derived from responses to questions concerning the person's place of birth (Question 9) and the place of birth of his or her parents (Question 25).
For more information on the place of birth questions in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definitions of Place of birth of respondent, Place of birth of father and Place of birth of mother.
Within the generation status variable, the three main categories are defined as follows:
'First generation' includes persons who were born outside Canada. For the most part, these are people who are now, or have ever been, immigrants to Canada.
'Second generation' includes persons who were born in Canada and had at least one parent born outside Canada. For the most part, these are the children of immigrants.
'Third generation or more' includes persons who were born in Canada with both parents born in Canada.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of generation status data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the language spoken most often or on a regular basis at home by the individual on May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Direct variable: Question 15, parts (a) and (b)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(a) asked 'What language does this person speak most often at home?' and Question 15(b) asked 'Does this person speak any other languages on a regular basis at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Part (a)
Report the language spoken most often at home. Report more than one language only if all languages are spoken equally often.
For a person who lives alone:
- report the language in which you feel most comfortable.
For a child who has not yet learned to speak:
- report the language spoken most often to this child at home. If two languages are spoken, report the language spoken most often. If both languages are used equally
often, report both languages.
Part (b)
Report any other languages that the person speaks at home on a regular basis, but not as often as the language reported in part (a).
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Direct variable: Question 15, parts (a) and (b)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(a) asked 'What language does this person speak most often at home?' and Question 15(b) asked 'Does this person speak any other languages on a regular basis at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Part (a)
Report the language spoken most often at home. Report more than one language only if all languages are spoken equally often.
For a person who lives alone:
- report the language in which you feel most comfortable.
For a child who has not yet learned to speak:
- report the language spoken most often to this child at home. If two languages are spoken, report the language spoken most often. If both languages are used equally
often, report both languages.
Part (b)
Report any other languages that the person speaks at home on a regular basis, but not as often as the language reported in part (a).
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the language spoken most often at home by the individual on May 10, 2011. Data on other languages spoken on a regular basis at home are also collected.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 15, part (a)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(a) asked 'What language does this person speak most often at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Report the language spoken most often at home. Report more than one language only if all languages are spoken equally often.
For a person who lives alone:
report the language in which you feel most comfortable. For a child who has not yet learned to speak:
report the language spoken most often to this child at home. If two languages are spoken, report the language spoken most often. If both languages are used equally
often, report both languages.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the
Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 15, part (a)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(a) asked 'What language does this person speak most often at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Report the language spoken most often at home. Report more than one language only if all languages are spoken equally often.
For a person who lives alone:
report the language in which you feel most comfortable. For a child who has not yet learned to speak:
report the language spoken most often to this child at home. If two languages are spoken, report the language spoken most often. If both languages are used equally
often, report both languages.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the
Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the other language(s) spoken on a regular basis at home by the individual on May 10, 2011. Data on language spoken most often at home were also collected.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 15, part (b)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(b) asked 'Does this person speak any other languages on a regular basis at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
Report any other languages that the person speaks at home on a regular basis, but not as often as the language reported in part (a).
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 15, part (b)
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 15(b) asked 'Does this person speak any other languages on a regular basis at home?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
Report any other languages that the person speaks at home on a regular basis, but not as often as the language reported in part (a).
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Immigrant status refers to whether the respondent is a non-immigrant, an immigrant or a non-permanent resident.
Non-immigrant refers to a person who is a Canadian citizen by birth.
Immigrant refers to a person who is or has ever been a landed immigrant/permanent resident. This person has been granted the right to live in Canada permanently by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens,
while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
Non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who has a work or study permit or who is a refugee claimant, and any non-Canadian-born family member living in Canada with them.
Non-immigrant refers to a person who is a Canadian citizen by birth.
Immigrant refers to a person who is or has ever been a landed immigrant/permanent resident. This person has been granted the right to live in Canada permanently by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens,
while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
Non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who has a work or study permit or who is a refugee claimant, and any non-Canadian-born family member living in Canada with them.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 10 and 11
Responses: Immigrant status is derived from the responses to the citizenship question (Question 10) and the landed immigrant status question (Question 11).
The standard classification for Immigrant status is 'Non-immigrants,' 'Immigrants' and 'Non-permanent residents.'
Remarks: In the 2011 National Household Survey, the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) and the citizenship question (Question 10) are used to identify non-immigrants (Canadian citizens by birth), immigrants and non-permanent residents.
The landed immigrant status question (Question 11) asked: "Is this person now, or has this person ever been, a landed immigrant?" Notes accompanying the landed immigrant question stated:
A 'landed immigrant' (permanent resident) is a person who has been granted the right to live in Canada permanently by immigration authorities.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons who are Canadian citizens by birth, foreign students, foreign workers, or refugee claimants, mark 'No.'
For persons who are Canadian citizens by naturalization or are permanent residents under the Immigration Act (permanent residents have been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by Canadian immigration authorities but have not yet obtained Canadian citizenship), mark 'Yes.'
Respondents who mark 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 10) are 'Immigrants.'
Respondents who mark 'No' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) are either 'Non-immigrants' or 'Non-permanent residents.' The citizenship question (Question 10) is used to derive the two groups. If a respondent is a Canadian citizen by birth according to Question 10, then he is a non-immigrant. If a respondent does not have Canadian citizenship and is not a landed immigrant, he is a non-permanent resident.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the citizenship question in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definition for Citizenship.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of immigrant status data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Questions 10 and 11
Responses: Immigrant status is derived from the responses to the citizenship question (Question 10) and the landed immigrant status question (Question 11).
The standard classification for Immigrant status is 'Non-immigrants,' 'Immigrants' and 'Non-permanent residents.'
Remarks: In the 2011 National Household Survey, the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) and the citizenship question (Question 10) are used to identify non-immigrants (Canadian citizens by birth), immigrants and non-permanent residents.
The landed immigrant status question (Question 11) asked: "Is this person now, or has this person ever been, a landed immigrant?" Notes accompanying the landed immigrant question stated:
A 'landed immigrant' (permanent resident) is a person who has been granted the right to live in Canada permanently by immigration authorities.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons who are Canadian citizens by birth, foreign students, foreign workers, or refugee claimants, mark 'No.'
For persons who are Canadian citizens by naturalization or are permanent residents under the Immigration Act (permanent residents have been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by Canadian immigration authorities but have not yet obtained Canadian citizenship), mark 'Yes.'
Respondents who mark 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 10) are 'Immigrants.'
Respondents who mark 'No' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) are either 'Non-immigrants' or 'Non-permanent residents.' The citizenship question (Question 10) is used to derive the two groups. If a respondent is a Canadian citizen by birth according to Question 10, then he is a non-immigrant. If a respondent does not have Canadian citizenship and is not a landed immigrant, he is a non-permanent resident.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the citizenship question in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definition for Citizenship.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of immigrant status data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to languages, other than English or French, in which the respondent can conduct a conversation.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 14
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.4: NHS classification of knowledge of non-official languages.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 14 asked ' What language(s), other than English or French, can this person speak well enough to conduct a conversation?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Report only those languages in which the person can carry on a conversation of some length on various topics.
For people who are deaf or have a speech disability, report knowledge of other languages, including sign language.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 14
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.4: NHS classification of knowledge of non-official languages.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 14 asked ' What language(s), other than English or French, can this person speak well enough to conduct a conversation?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Report only those languages in which the person can carry on a conversation of some length on various topics.
For people who are deaf or have a speech disability, report knowledge of other languages, including sign language.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the ability to conduct a conversation in English only, in French only, in both English and French, or in neither English nor French.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 13
Responses: English only; French only; Both English and French; Neither English nor French
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 13 asked ' Can this person speak English or French well enough to conduct a conversation?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Mark English or French only if the person can carry on a conversation of some length on various topics in that language.
For people who are deaf or have a speech disability, report knowledge of English, French, or both.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 13
Responses: English only; French only; Both English and French; Neither English nor French
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 13 asked ' Can this person speak English or French well enough to conduct a conversation?'
Instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS guide:
Mark English or French only if the person can carry on a conversation of some length on various topics in that language.
For people who are deaf or have a speech disability, report knowledge of English, French, or both.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Refers to the first language learned at home in childhood and still understood by the individual on May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 16
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 16 asked 'What is the language that this person first learned at home in childhood and still understands?'
A note accompanying the question stated that:
If this person no longer understands the first language learned, indicate the second language learned.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7 Mother tongue and home language

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7A Aboriginal languages
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7B Germanic languages
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7D Afro-Asiatic languages
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7F Sino-Tibetan languages

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 16
Responses: See Figures 1.7, 1.7A, 1.7B, 1.7C, 1.7D, 1.7E and 1.7F.
See Appendix 1.3: NHS classification of mother tongue, home language and language of work.
Remarks: In the 2011 NHS, Question 16 asked 'What is the language that this person first learned at home in childhood and still understands?'
A note accompanying the question stated that:
If this person no longer understands the first language learned, indicate the second language learned.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
- For a person who learned two languages at the same time in early childhood, report the language this person spoke most often at home before starting school. Report two languages only if both languages were used equally often and are still understood by this person.
- For a child who has not yet learned to speak, report the language spoken most often to the child at home. Report two languages only if both languages are spoken equally often so that the child learns both languages at the same time.
The order of response options in language questions which have mark-ins for 'English' and 'French' is different depending on the language of the questionnaire. On English questionnaires, 'English' is listed before 'French.' On French questionnaires, 'French' is listed before English. In a similar way, the language of the questionnaire is the language mentioned first in the actual wording of the questions on knowledge of official and non-official languages.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of data on language, refer to the Languages Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7 Mother tongue and home language

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7A Aboriginal languages

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7B Germanic languages

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7D Afro-Asiatic languages

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.7F Sino-Tibetan languages

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Period of immigration refers to the period in which the immigrant first obtained his or her landed immigrant/permanent resident status.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question no.: Derived variable: Question 12
Responses: Ranges of years for the years 1901 to 2011.
For the immigrant population, period of immigration is derived from Year of immigration (Question 12).
Typically, single years of immigration are collapsed to form larger categories of five or ten years.
Remarks: Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Persons who were unable to give the exact year of immigration were asked to give the best possible estimate. People who immigrated to Canada more than once were to report the year in which they first received landed immigrant status.
Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12).
These people include Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) and non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who is living in Canada on a work or study permit or as a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living with him or her.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status and Year of immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of period of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question no.: Derived variable: Question 12
Responses: Ranges of years for the years 1901 to 2011.
For the immigrant population, period of immigration is derived from Year of immigration (Question 12).
Typically, single years of immigration are collapsed to form larger categories of five or ten years.
Remarks: Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Persons who were unable to give the exact year of immigration were asked to give the best possible estimate. People who immigrated to Canada more than once were to report the year in which they first received landed immigrant status.
Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12).
These people include Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) and non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who is living in Canada on a work or study permit or as a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living with him or her.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status and Year of immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of period of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Place of birth of father refers to the name of country in which the respondent's father was born. The geographic location is specified according to boundaries current at the time the data are collected, not the boundaries at the time of birth.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 25(a)
Responses: Response categories included a mark-in circle for 'Born in Canada' and a write-in space for 'Born outside Canada - Specify country.'
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth of father disseminated in the National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth of parents question is: 'Where was each of this person's parents born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate the place of birth of their father according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, a respondent whose father was born in an area which, at the time of his birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan was asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
- report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
-report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
- report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
-report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive Generation status.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 25(a)
Responses: Response categories included a mark-in circle for 'Born in Canada' and a write-in space for 'Born outside Canada - Specify country.'
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth of father disseminated in the National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth of parents question is: 'Where was each of this person's parents born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate the place of birth of their father according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, a respondent whose father was born in an area which, at the time of his birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan was asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
- report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
-report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
- report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
-report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive Generation status.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Place of birth of mother refers to the name of the country in which the mother of the respondent was born. The geographic location is specified according to boundaries current at the time the data are collected, not the boundaries at the time of birth.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 25(b)
Responses: Response categories included a mark-in circle for 'Born in Canada' and a write-in space for 'Born outside Canada - Specify country.'
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth of mother disseminated in the National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth of parents question is: 'Where was each of this person's parents born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate the place of birth of their mother according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, a respondent whose mother was born in an area which, at the time of his birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan was asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
-report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
- report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
-report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
- report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive Generation status.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 25(b)
Responses: Response categories included a mark-in circle for 'Born in Canada' and a write-in space for 'Born outside Canada - Specify country.'
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth of mother disseminated in the National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth of parents question is: 'Where was each of this person's parents born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate the place of birth of their mother according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, a respondent whose mother was born in an area which, at the time of his birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan was asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
-report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
- report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
-report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
- report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive Generation status.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Place of birth refers to the name of the province, territory or country in which the person was born. It may refer to a province or territory if the person was born in Canada. It refers to a country if the person was born outside Canada. The geographic location is specified according to boundaries current at the time the data are collected, not the boundaries at the time of birth.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 9
Responses: Response categories included 13 mark-in circles representing each province and territory of Canada for those 'Born in Canada' and one write-in space where those 'Born outside Canada' could specify their country of birth.
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth disseminated in the 2011 National Household Survey.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth question is: 'Where was this person born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate their place of birth according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, respondents born in an area which, at the time of their birth, was part of the Northwest Territories but which is now part of the territory of Nunavut were asked to write 'Nunavut'; respondents born in an area which, at the time of their birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan were asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
-report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
-report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
- report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
-report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive the Generation status variable.
For additional information on place of birth responses, refer to Figure 1.5.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.5 Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents - Place of birth
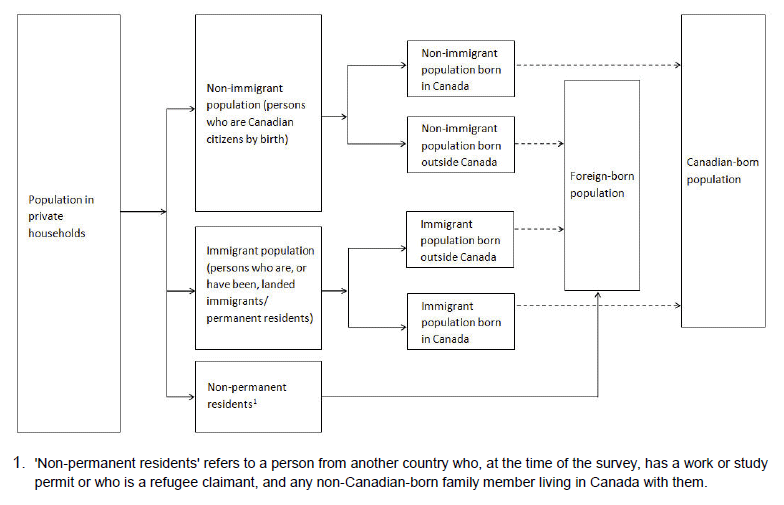
Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 9
Responses: Response categories included 13 mark-in circles representing each province and territory of Canada for those 'Born in Canada' and one write-in space where those 'Born outside Canada' could specify their country of birth.
Refer to Appendix 1.5 for the places of birth disseminated in the 2011 National Household Survey.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS Place of birth question is: 'Where was this person born?'
Respondents were asked to indicate their place of birth according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011, the reference date for the National Household Survey. For example, respondents born in an area which, at the time of their birth, was part of the Northwest Territories but which is now part of the territory of Nunavut were asked to write 'Nunavut'; respondents born in an area which, at the time of their birth, was part of the USSR but which is now part of Kazakhstan were asked to write 'Kazakhstan'.
As well, additional instructions were provided to respondents in the 2011 NHS Guide:
For persons born in any of the six counties of Northern Ireland:
-report 'United Kingdom.'
For persons born in one of the counties of the Republic of Ireland:
-report 'Republic of Ireland.'
For persons born in the former U.S.S.R., the former Yugoslavia or the former Czechoslovakia:
- report the name of the independent country or republic according to the boundaries in existence on May 10, 2011. For example, a person who was born in the former
U.S.S.R. should report the specific country or republic that is now a nation state-Ukraine, Latvia, Russia, etc.
For persons who are not sure of the country because its boundaries have changed since the time of birth:
-report the name of the nearest city, state or province.
For adopted persons:
-report the place of birth of their adoptive parents if place of birth is unknown for the adopted person or for the adopted person's birth parents.
The place of birth of respondent, place of birth of father and place of birth of mother questions are used to derive the Generation status variable.
For additional information on place of birth responses, refer to Figure 1.5.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of place of birth data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Figure 1.5 Immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents - Place of birth

Source: Statistics Canada, National Household Survey, 2011.
Population group refers to the population group or groups to which the person belongs, for example, White, South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean or Japanese.
These population groups are the groups used on the 2011 National Household Survey questionnaire to collect data on the visible minority population for employment equity purposes. The Employment Equity Act defines visible minorities as 'persons, other than Aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in
colour.'
These population groups are the groups used on the 2011 National Household Survey questionnaire to collect data on the visible minority population for employment equity purposes. The Employment Equity Act defines visible minorities as 'persons, other than Aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in
colour.'
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Question 19 and Question 18
Responses: The Population group variable is derived from information collected in Question 19: Population group and Question 18: Aboriginal group. Persons who reported 'Yes, First Nations (North American Indian),' 'Yes, Métis' or 'Yes, Inuk (Inuit)' to Question 18 (Aboriginal peoples) were not asked the population group question but are included in the 'Not a visible minority' category in the Visible minority variable, along with persons reporting other selected groups such as 'White.' All other respondents are classified according to their population group as reported in Question 19.
In Question 19: Population group, respondents were asked to use one or more of the mark-in circles provided to indicate their population group(s). The following mark-in circles were provided on the questionnaire: White, South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese. A write-in space was also provided for respondents who wanted to specify a population group not included in the list of mark-in circles.
For additional information on the NHS classification of Population group, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: Population group refers to the population group or groups to which the person belongs. The population group question is used to derive estimates for the visible minority population, as defined by the Employment Equity Act. The Employment Equity Act defines visible minorities as 'persons, other than Aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour.'
For information on the Visible minority variable that is derived from the population group question, refer to the definition 'Visible minority.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of population group data, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Question 19 and Question 18
Responses: The Population group variable is derived from information collected in Question 19: Population group and Question 18: Aboriginal group. Persons who reported 'Yes, First Nations (North American Indian),' 'Yes, Métis' or 'Yes, Inuk (Inuit)' to Question 18 (Aboriginal peoples) were not asked the population group question but are included in the 'Not a visible minority' category in the Visible minority variable, along with persons reporting other selected groups such as 'White.' All other respondents are classified according to their population group as reported in Question 19.
In Question 19: Population group, respondents were asked to use one or more of the mark-in circles provided to indicate their population group(s). The following mark-in circles were provided on the questionnaire: White, South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese. A write-in space was also provided for respondents who wanted to specify a population group not included in the list of mark-in circles.
For additional information on the NHS classification of Population group, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: Population group refers to the population group or groups to which the person belongs. The population group question is used to derive estimates for the visible minority population, as defined by the Employment Equity Act. The Employment Equity Act defines visible minorities as 'persons, other than Aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour.'
For information on the Visible minority variable that is derived from the population group question, refer to the definition 'Visible minority.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of population group data, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Religion refers to the person's self-identification as having a connection or affiliation with any religious denomination, group, body, sect, cult or other religiously defined community or system of belief. Religion is not limited to formal membership in a religious organization or group. Persons without a religious connection or affiliation can self-identify as atheist, agnostic or humanist, or can provide another applicable response.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Question 22
Responses: Respondents were asked to specify one denomination or religion only in Question 22.
Two lines were provided for a write-in response and respondents could also mark a circle for 'No religion.' Refer to Appendix 1.7 for the 2011 National Household Survey classification for religion.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS religion question asked: 'What is this person's religion?' Notes accompanying the religion question advised respondents to:
Indicate a specific denomination or religion even if this person is not currently a practising member of that group.
For example, Roman Catholic, United Church, Anglican, Baptist, Lutheran, Muslim, Presbyterian, Pentecostal, Jewish, Buddhist, Hindu, Sikh, Greek Orthodox, etc.
The 2011 NHS Guide stated that:
In the answer box provided, respondents should write the name of the specific denomination or religion with which they identify, even if they are not currently a practising member of that group.
A person who has no religious affiliation can either choose to mark the circle for 'No religion' or to print other responses, such as 'Atheist' (does not believe in the existence of God) or 'Agnostic' (believes nothing can be known about the existence of God) in the write-in box.
For infants or children, report the denomination or religion in which they will be raised.
For persons who are members of a specific group within a larger religion, report the particular name or term for the specific group.
Respondents should indicate what they feel best describes their religious affiliation. For additional information on issues related to the collection and dissemination of religion data, refer to the Religion Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question no.: Question 22
Responses: Respondents were asked to specify one denomination or religion only in Question 22.
Two lines were provided for a write-in response and respondents could also mark a circle for 'No religion.' Refer to Appendix 1.7 for the 2011 National Household Survey classification for religion.
Remarks: The 2011 NHS religion question asked: 'What is this person's religion?' Notes accompanying the religion question advised respondents to:
Indicate a specific denomination or religion even if this person is not currently a practising member of that group.
For example, Roman Catholic, United Church, Anglican, Baptist, Lutheran, Muslim, Presbyterian, Pentecostal, Jewish, Buddhist, Hindu, Sikh, Greek Orthodox, etc.
The 2011 NHS Guide stated that:
In the answer box provided, respondents should write the name of the specific denomination or religion with which they identify, even if they are not currently a practising member of that group.
A person who has no religious affiliation can either choose to mark the circle for 'No religion' or to print other responses, such as 'Atheist' (does not believe in the existence of God) or 'Agnostic' (believes nothing can be known about the existence of God) in the write-in box.
For infants or children, report the denomination or religion in which they will be raised.
For persons who are members of a specific group within a larger religion, report the particular name or term for the specific group.
Respondents should indicate what they feel best describes their religious affiliation. For additional information on issues related to the collection and dissemination of religion data, refer to the Religion Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Visible minority refers to whether a person belongs to a visible minority group as defined by the Employment Equity Act and, if so, the visible minority group to which the person belongs. The Employment Equity Act defines visible minorities as 'persons, other than Aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in
colour.' The visible minority population consists mainly of the following groups: South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese.
colour.' The visible minority population consists mainly of the following groups: South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Question 19 and Question 18
Responses: The Visible minority variable is derived from information collected in Question 19: Population group and Question 18: Aboriginal group. Persons who reported 'Yes, First Nations (North American Indian),' 'Yes, Métis' or 'Yes, Inuk (Inuit)' to Question 18 (Aboriginal peoples) were not asked the Population group question but are included in the 'Not a visible minority' category in the Visible minority variable, along with persons reporting other selected groups such as 'White.' All other respondents are classified according to their population group as reported in Question 19.
In Question 19: Population group, respondents were asked to use one or more of the mark-in circles boxes provided to indicate their population group(s). The following mark-in circles were provided on the questionnaire: White, South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese. A write-in space was also provided for respondents who wanted to specify a population group not included in the list of mark-in circles.
For additional information on the NHS classificaiton of Visible minority, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: Visible minority refers to whether a person belongs to a visible minority group as defined by the Employment Equity Act and, if so, the visible minority group to which the person belongs. Visible minority is derived from population group (Question 19) and Aboriginal group (Question 18). For information on the population group question in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definition 'Population group.'
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of visible minority data, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Population in private households
Question nos.: Derived variable: Question 19 and Question 18
Responses: The Visible minority variable is derived from information collected in Question 19: Population group and Question 18: Aboriginal group. Persons who reported 'Yes, First Nations (North American Indian),' 'Yes, Métis' or 'Yes, Inuk (Inuit)' to Question 18 (Aboriginal peoples) were not asked the Population group question but are included in the 'Not a visible minority' category in the Visible minority variable, along with persons reporting other selected groups such as 'White.' All other respondents are classified according to their population group as reported in Question 19.
In Question 19: Population group, respondents were asked to use one or more of the mark-in circles boxes provided to indicate their population group(s). The following mark-in circles were provided on the questionnaire: White, South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, Latin American, Arab, Southeast Asian, West Asian, Korean and Japanese. A write-in space was also provided for respondents who wanted to specify a population group not included in the list of mark-in circles.
For additional information on the NHS classificaiton of Visible minority, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Remarks: Visible minority refers to whether a person belongs to a visible minority group as defined by the Employment Equity Act and, if so, the visible minority group to which the person belongs. Visible minority is derived from population group (Question 19) and Aboriginal group (Question 18). For information on the population group question in the 2011 National Household Survey, refer to the definition 'Population group.'
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of visible minority data, refer to the Visible Minority and Population Group Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Year of immigration refers to the year in which the immigrant first obtained his or her landed immigrant/permanent resident status.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are
born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
A landed immigrant/permanent resident is a person who has been granted the right to live permanently in Canada by immigration authorities. Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. Some immigrants are Canadian citizens, while others are not. Most immigrants are
born outside Canada, but a small number are born in Canada. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' includes immigrants who landed in Canada prior to May 10, 2011.
Reported in: 2011
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 12
Responses: Single years from 1901 to 2011
Remarks: Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Persons who were unable to give the exact year of immigration were asked to give the best possible estimate. People who immigrated to Canada more than once were to report the year in which they first received landed immigrant status.
Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12).
These people include Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) and non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who is living in Canada on a work or study permit or as a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living with him or her.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status, Period of immigration and Age at immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of year of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.
Reported for: Persons in private households who are, or have ever been, landed immigrants
Question no.: Direct variable: Question 12
Responses: Single years from 1901 to 2011
Remarks: Respondents who answered 'Yes' to the landed immigrant status question (Question 11) were asked to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12) by reporting the year in which they first obtained landed immigrant status. Persons who were unable to give the exact year of immigration were asked to give the best possible estimate. People who immigrated to Canada more than once were to report the year in which they first received landed immigrant status.
Some immigrants have resided in Canada for a number of years, while others have arrived recently. In the 2011 National Household Survey, 'Immigrants' refers to immigrants who landed in Canada before the reference date, May 10, 2011.
Respondents who answered 'No' to Question 11 will not have gone through the immigration process and, thus, did not have to answer the year of immigration question (Question 12).
These people include Canadian citizens by birth (non-immigrants) and non-permanent residents. A non-permanent resident refers to a person from another country who is living in Canada on a work or study permit or as a refugee claimant, and any foreign-born family member living with him or her.
For further information on immigrants, non-immigrants and non-permanent residents, refer to Figures 1.5 and 1.6.
For more information on the other immigration variables, refer to the definitions for Immigrant status, Period of immigration and Age at immigration.
For additional information on the collection and dissemination of year of immigration data, refer to the Place of Birth, Generation Status, Citizenship and Immigration Reference Guide, National Household Survey, 2011.




